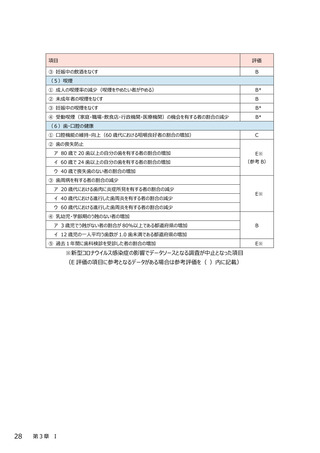
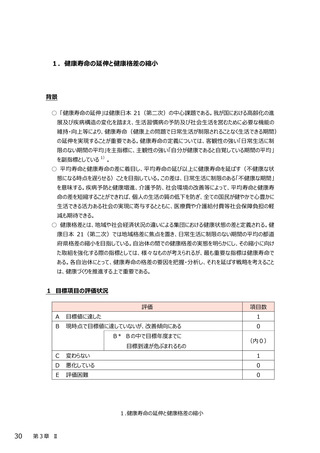
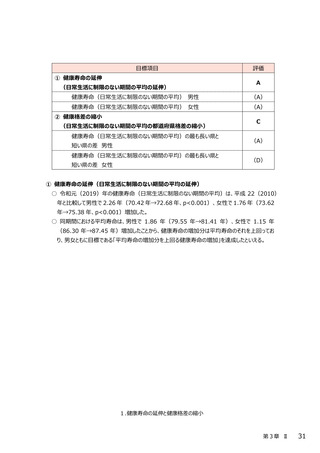
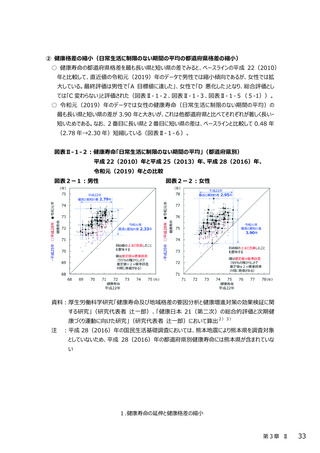
最終評価報告書 第3章(Ⅰ~Ⅱ4) (120 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_28410.html |
| 出典情報 | 健康日本21(第二次)最終評価報告書を公表します(10/11)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
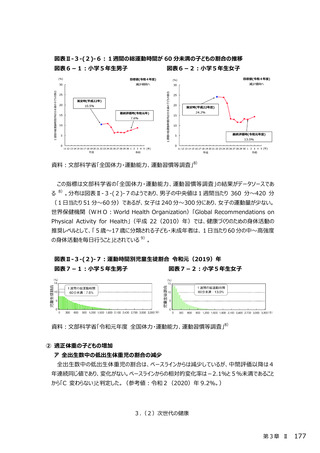
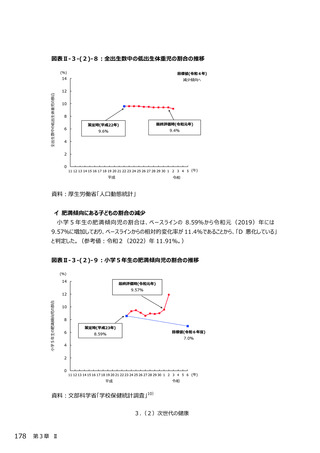
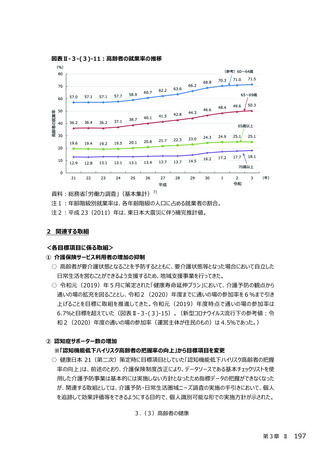
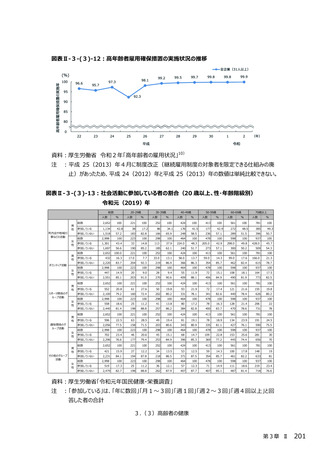
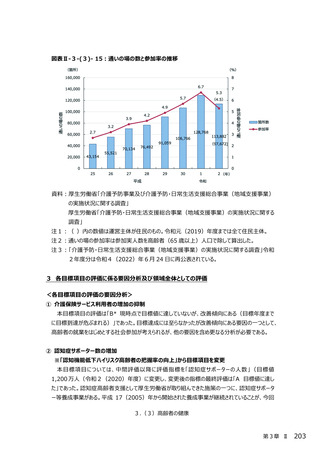
○ 新型コロナウイルス感染症による健診受診控えに対してリーフレット等を通した啓発により、受診
勧奨を⾏っている。
<参考⽂献・URL>
1) Yokoyama H, Araki SI, Kawai K, Yamazaki K, Tomonaga O, Shirabe SI, et al.
Declining trends of diabetic nephropathy, retinopathy and neuropathy with
improving diabetes care indicators in Japanese patients with type 2 and type 1
diabetes (JDDM 46). BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2018;6(1):e000521. Epub
20180529. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2018-000521. PubMed PMID: 29892340;
PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5992467.
2) Kawasaki R, Tanaka S, Yamamoto T, Sone H, Ohashi Y, Akanuma Y, et al.
Incidence and progression of diabetic retinopathy in Japanese adults with type 2
diabetes: 8 year follow-up study of the Japan Diabetes Complications Study
(JDCS). Diabetologia. 2011;54(9):2288-94. Epub 20110601. doi: 10.1007/
s00125-011-2199-0. PubMed PMID: 21630126.
3) Sone H, Tanaka S, Suzuki S, Seino H, Hanyu O, Sato A, et al. Leisure-time physical
activity is a significant predictor of stroke and total mortality in Japanese patients
with type 2 diabetes: analysis from the Japan Diabetes Complications Study
(JDCS). Diabetologia. 2013;56(5):1021-30. Epub 20130227. doi: 10.1007/
s00125-012-2810-z. PubMed PMID: 23443242.
4)
Xue M, Xu W, Ou YN, Cao XP, Tan MS, Tan L, et al. Diabetes mellitus and risks
of cognitive impairment and dementia: A systematic review and metaanalysis of 144 prospective studies. Ageing Res Rev. 2019;55:100944. Epub
20190817. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2019.100944. PubMed PMID: 31430566.
5) Sasazuki S, Charvat H, Hara A, Wakai K, Nagata C, Nakamura K, et al. Diabetes
mellitus and cancer risk: pooled analysis of eight cohort studies in Japan. Cancer
Sci. 2013;104(11):1499-507. Epub 20130825. doi: 10.1111/cas.12241. PubMed
PMID: 23889822; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC7656560.
6) Williams R, Karuranga S, Malanda B, Saeedi P, Basit A, Besançon S, et al. Global
and regional estimates and projections of diabetes-related health expenditure:
Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition.
Diabetes
Res
Clin
Pract.
2020;162:108072.
Epub
20200213.
doi:
10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108072. PubMed PMID: 32061820.
7) Gregg E, et al. WHO: the Diabetes Targets Expert Consultation Group. Improving
Health Outcomes of People with Diabetes Mellitus; Target Setting to Reduce the
Global Burden of Diabetes Mellitus by 2030.World Health Organization,2021.
https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/improving-health-outcomes-ofpeople-with-diabetes-mellitus
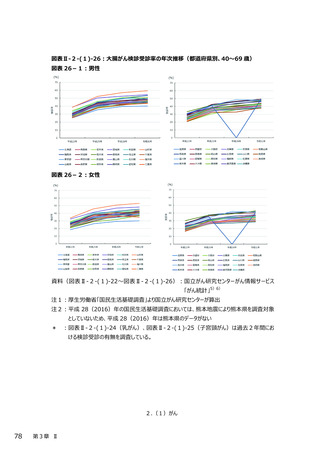
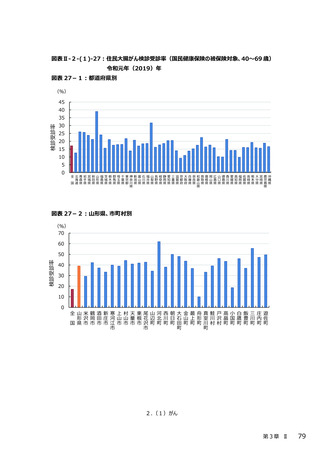
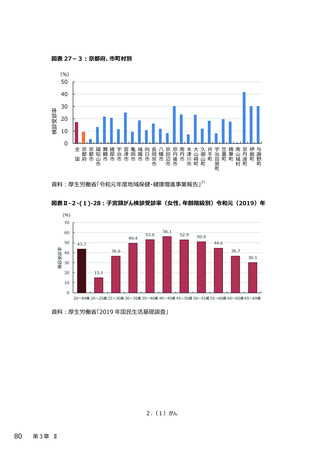
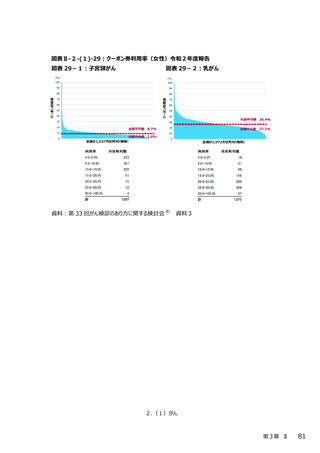
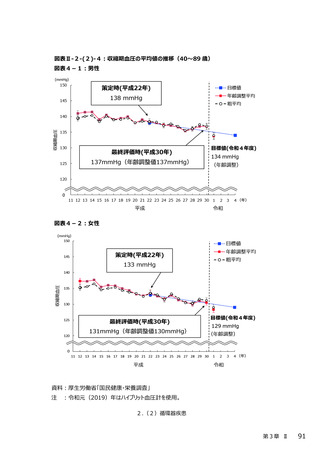
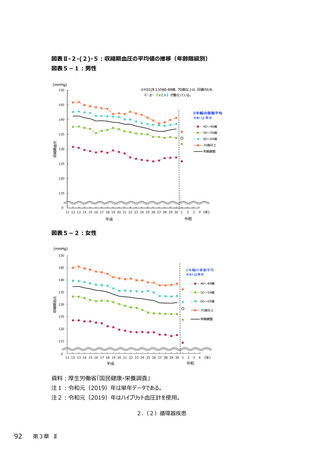
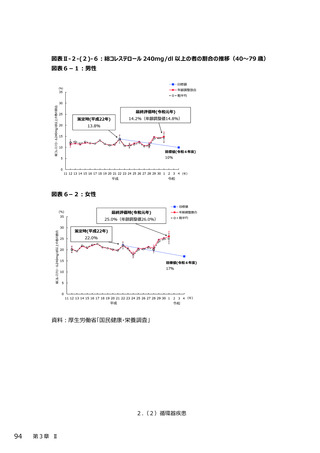
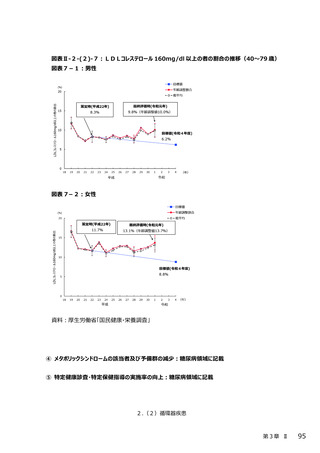
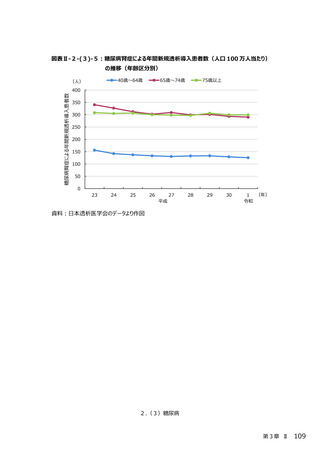
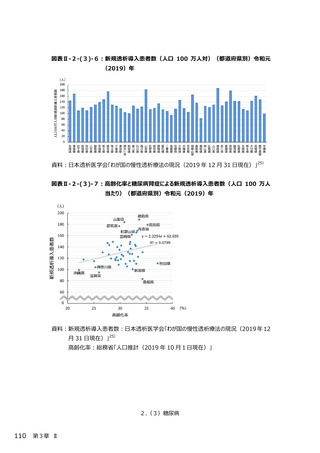
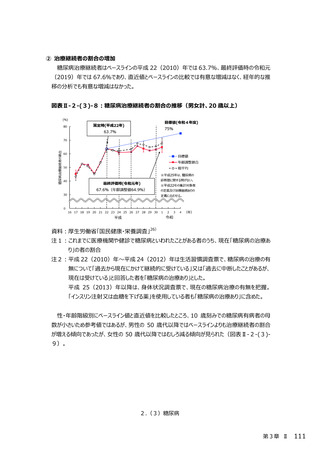
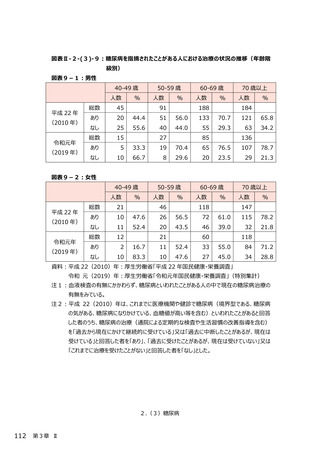
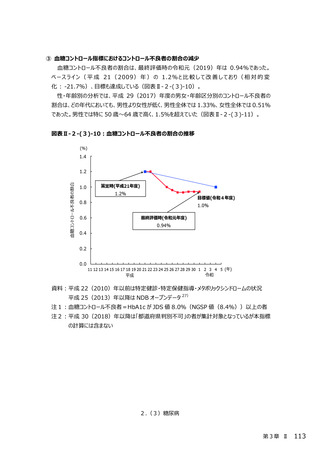
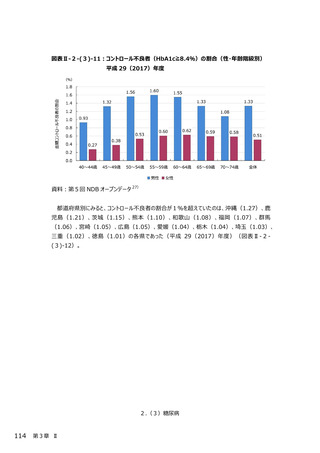
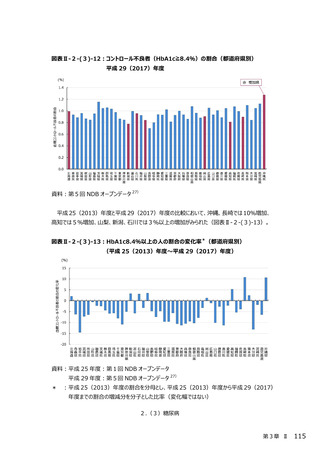
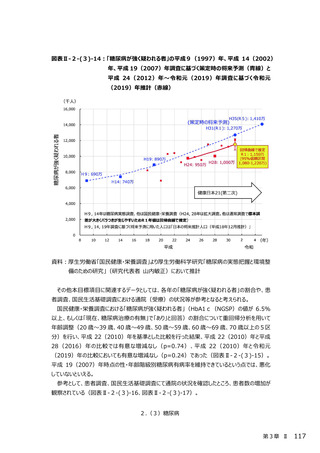
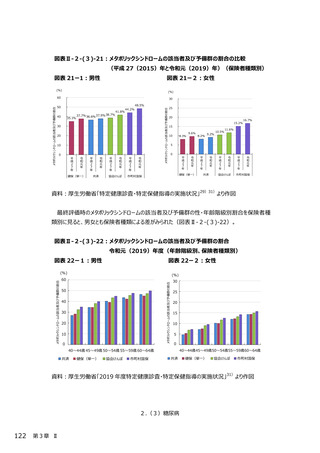
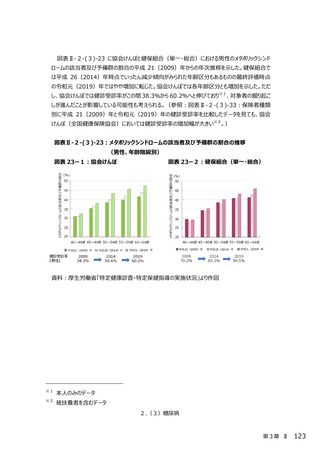
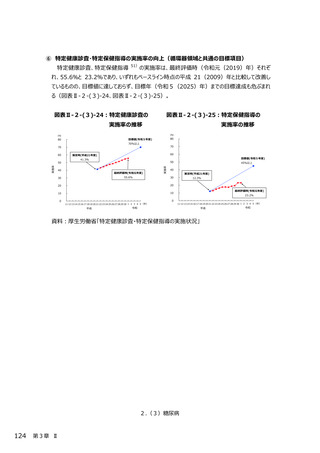
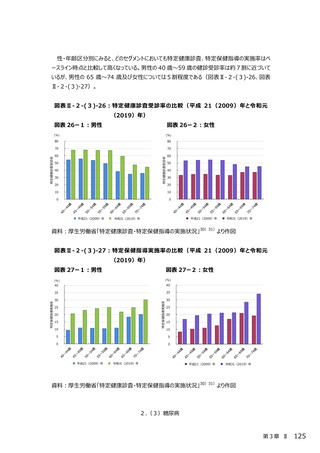
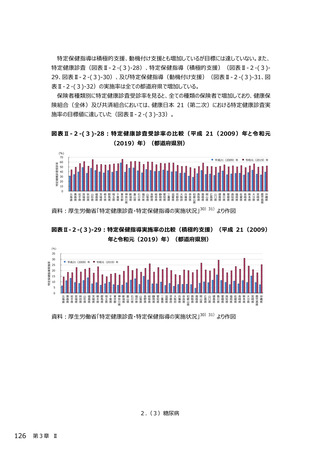
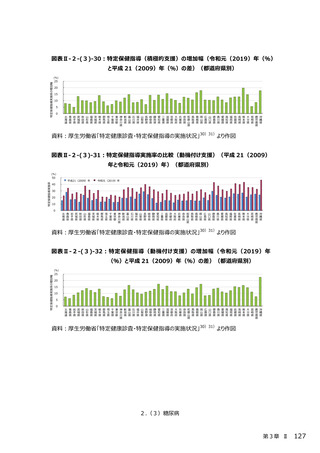
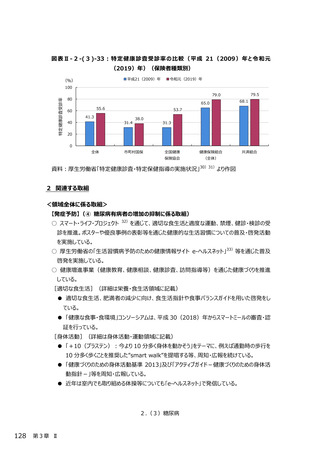
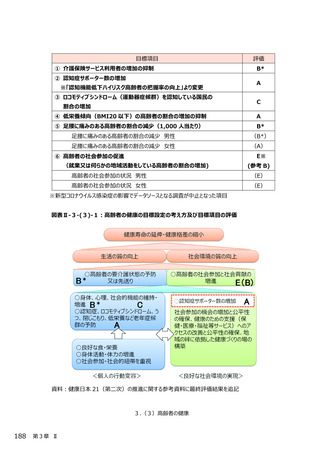
2.(3)糖尿病
142
第3章 Ⅱ