資料5-1 Ⅳ-203 モキシフロキサシン塩酸塩[15.1MB] (122 ページ)
出典
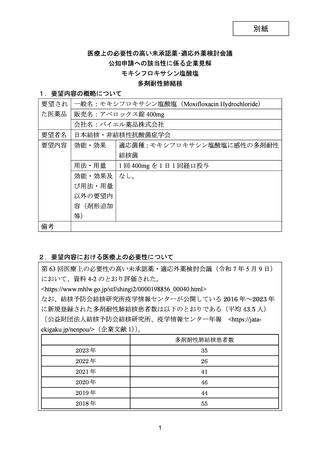
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/shingi2/0000198856_00044.html |
| 出典情報 | 医療上の必要性の高い未承認薬・適応外薬検討会議(第66回 12/12)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
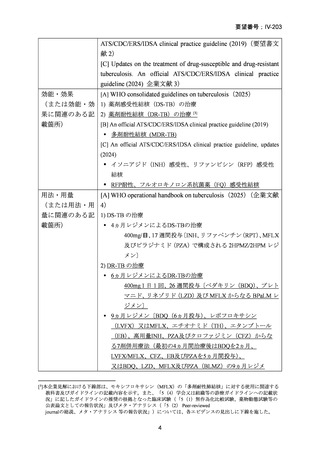
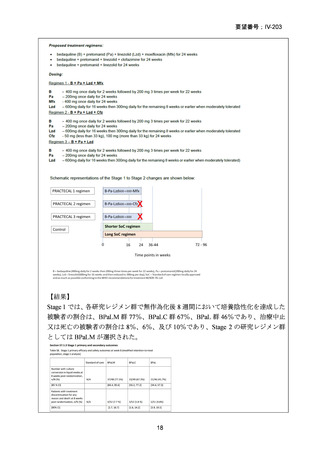
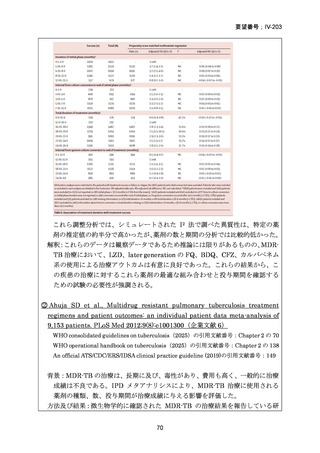
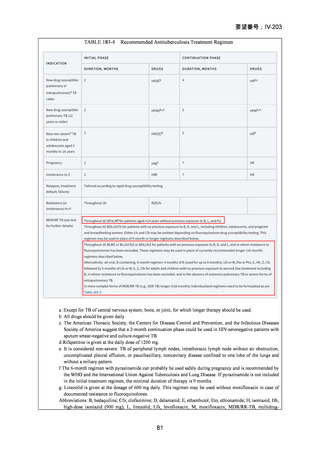
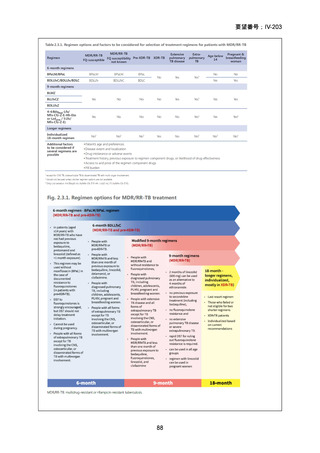
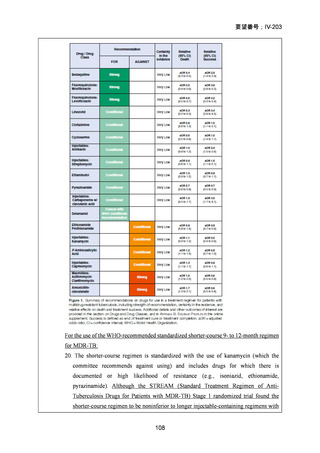
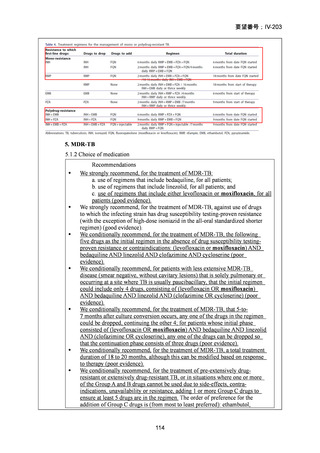
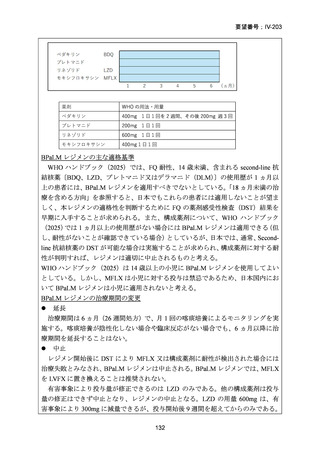
Bedaquiline is usually ceased at 6 months (WHO); but can be considered
for use up to 5–7 months post sputum culture conversion
(ATS/CDC/ERS/IDSA).
The continuation phase should comprise at least 3 drugs (WHO); or 4
drugs (ATS/CDC/ERS/IDSA).
Total duration of treatment should be 18–20 months (or at least 15–
17 months post culture conversion) but can be adjusted according to
treatment response determined by clinical, bacteriological and
radiological parameters (WHO); ATS/CDC/ERS/IDSA suggest 15–
21 months post culture conversion to define duration.
In an MDR-TB case with additional fluoroquinolone resistance (or where
one or more group A or B agents cannot be used), prolonged use of
bedaquiline should be considered in addition to the selection of a group C
agent(s) as prioritised to ensure a 5-drug regimen.
In a case of XDR-TB, the same approach to drug selection should be
followed
(小児に関する推奨内容は省略)
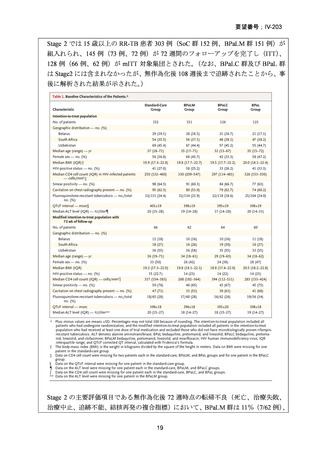
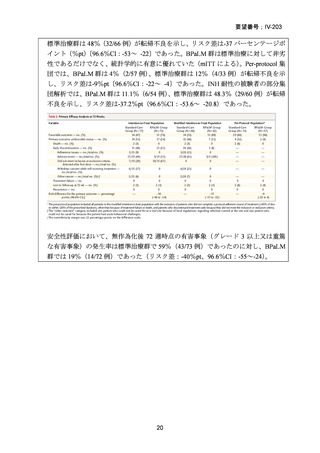
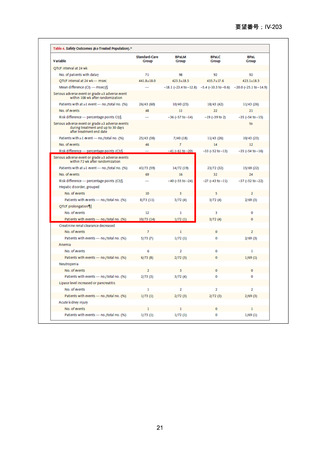
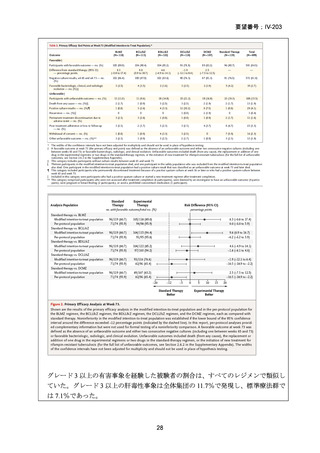
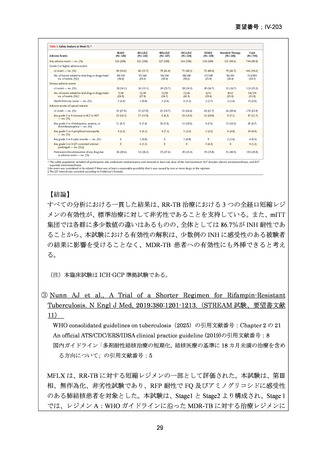
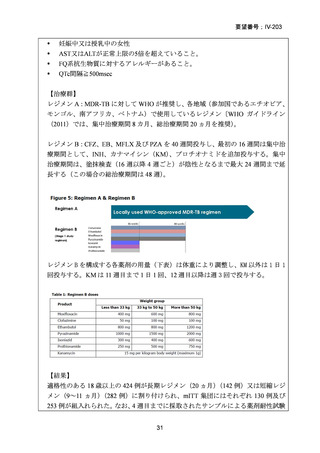
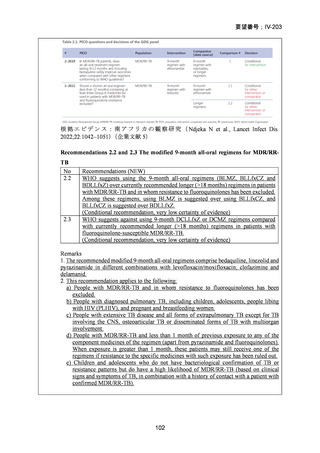
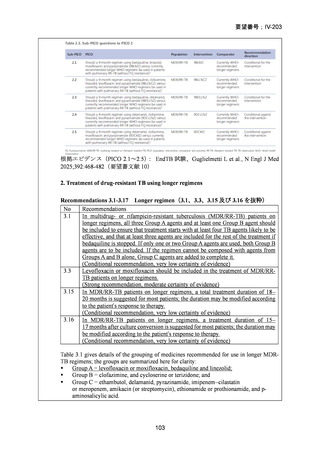
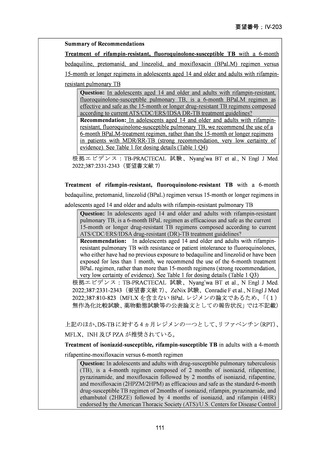
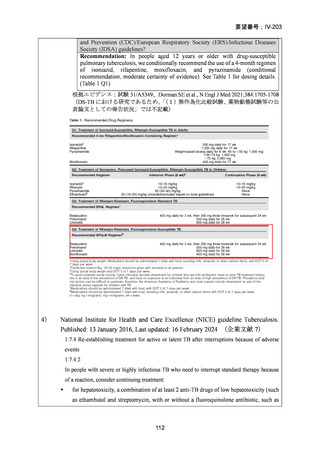
根拠エビデンス(BPaLM レジメン):TB-PRACTECAL 試験、Nyang’wa BT et al., N Engl
J Med. 2022;387:2331-2343(要望書文献 7)
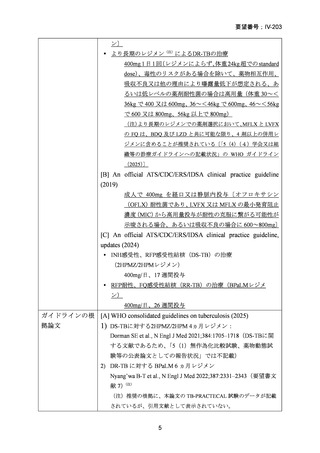
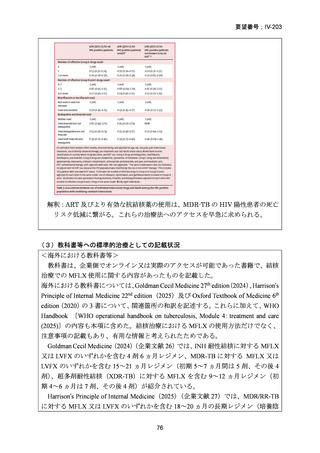
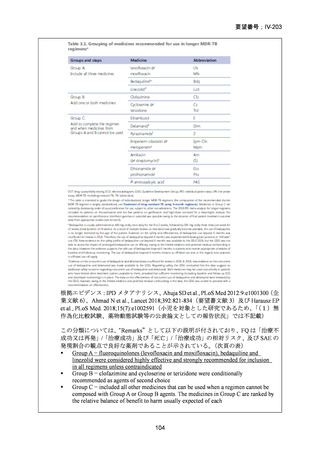
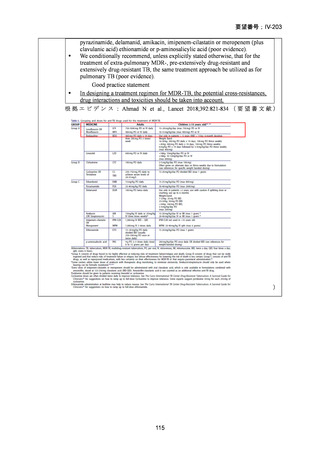
Isoniazid mono-resistance (rifampicin susceptible)
WHO guidance on management of isoniazid resistant but rifampicin susceptible TB has
been in place since 2018 and includes the following:
1. A combination of rifampicin, ethambutol, pyrazinamide and levofloxacin
or moxifloxacin (levofloxacin preferred) for 6 months.
2. If disease is severe, 9 months is advised.
3. If low-level isoniazid resistance is confirmed, the use of high dose isoniazid
can be considered.
The ATS/CDC/ERS/IDSA guidance also suggests that pyrazinamide can be ceased after
two months in those with less severe disease. If a fluoroquinolone cannot be used, the
previously recommended combination of rifampicin, ethambutol and pyrazinamide
(with or without high dose isoniazid) for 6–9 months is still considered acceptable
particularly in less severe disease.
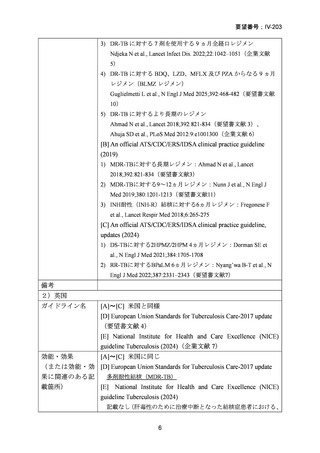
Rifampicin mono-resistance (isoniazid susceptible)
The WHO advise the same treatment for both rifampicin mono-resistant TB (RR-TB)
and MDR-TB. Although isoniazid is a potent bactericidal drug and theoretically still
available for treatment, the most recent ATS/CDC/ERS/IDSA guidelines also make no
118