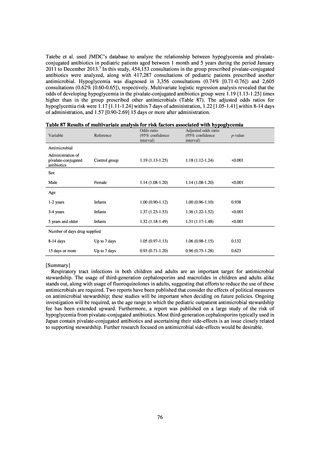
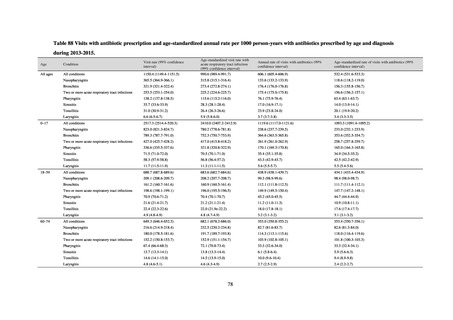
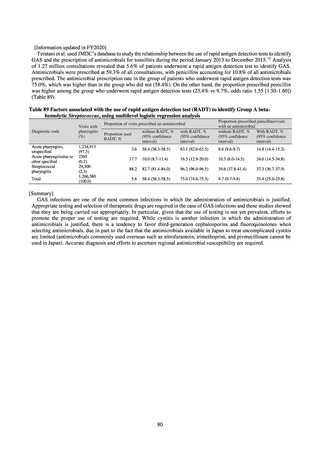
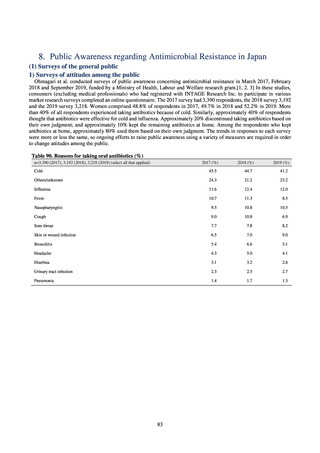
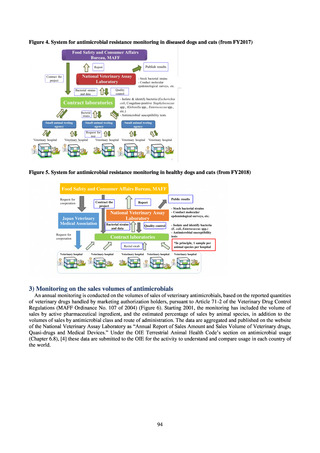
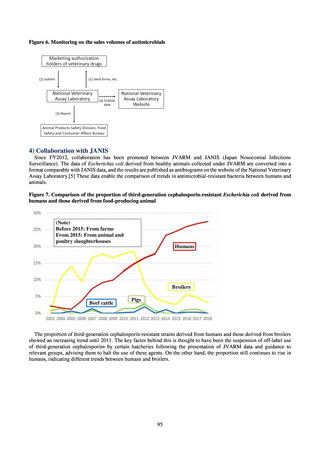
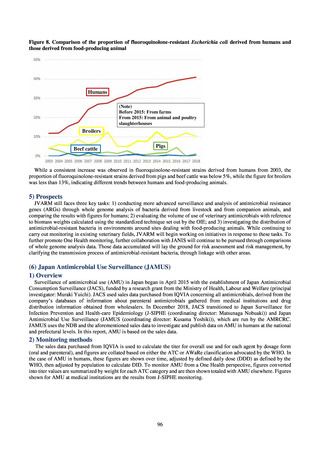
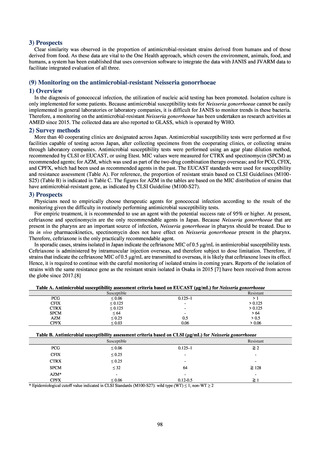
よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
【参考資料3】【英版R4.1.17】Nippon AMR One Health Report (NAOR) 2020 (98 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_23261.html |
| 出典情報 | 国際的に脅威となる感染症対策関係閣僚会議 薬剤耐性ワンヘルス動向調査検討会(第9回 1/17)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
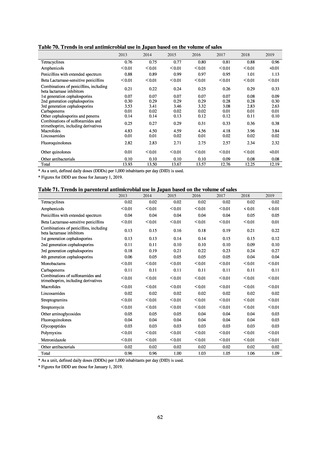
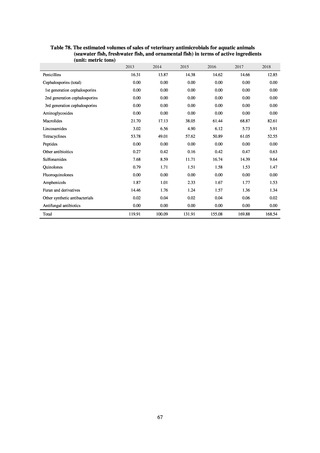
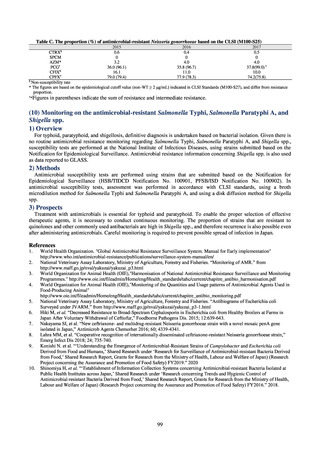
3) Prospects
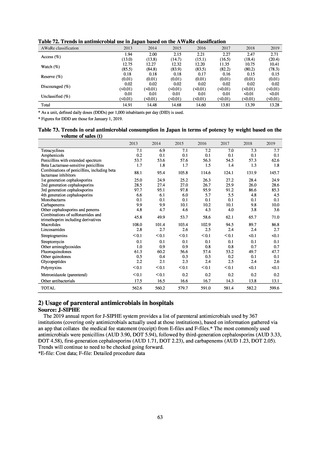
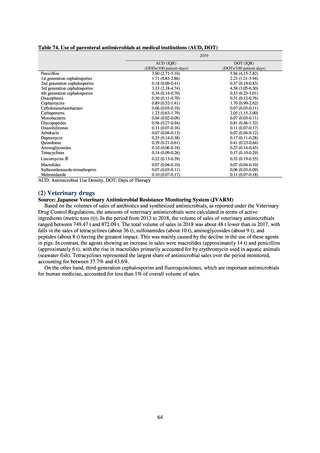
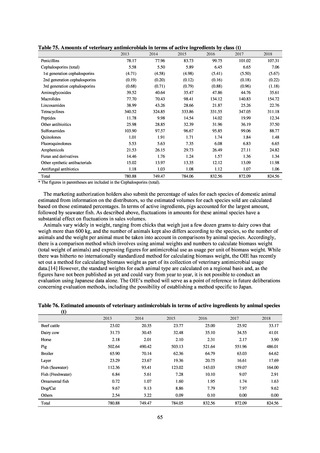
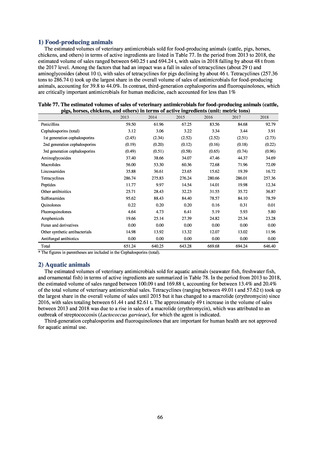
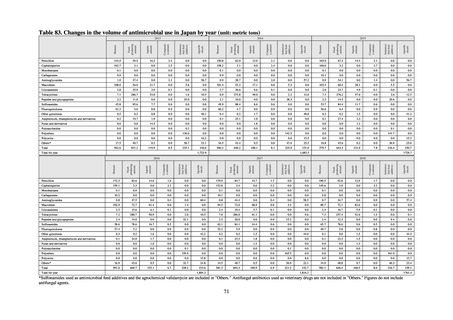
The establishment of Japan’s first AMU surveillance programs in the form of JAMUS and J-SIPHE put in place a system
that enables trends in AMU over time to be fed back to the public. While sources of AMU information include both data
on the volume of sales and insurance billing data, this report focuses on sales data. This is because: 1) it is an international
standard; 2) using different sources of information to show information for the same purpose, namely AMU, will confuse
the reader; and 3) the outcome indices in the National Action Plan on AMR are based on the results of surveillance of sales
volumes. The sources of information used and the way in which they are presented need to be altered according to their
purpose and further consideration is required regarding the form in which they should be collated and fed back on an
ongoing basis.
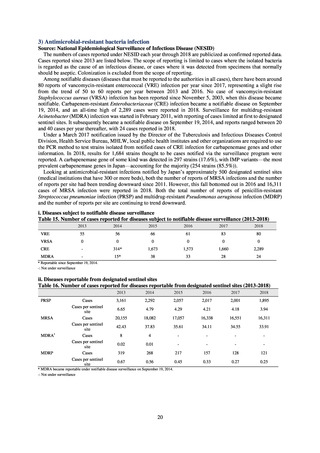
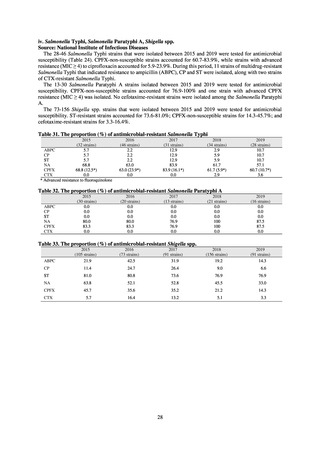
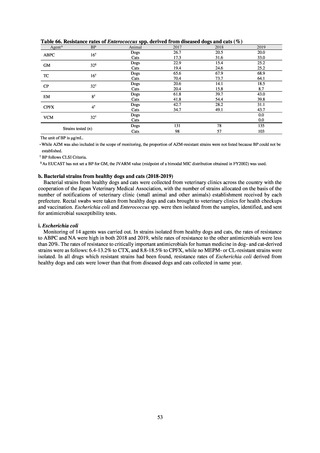
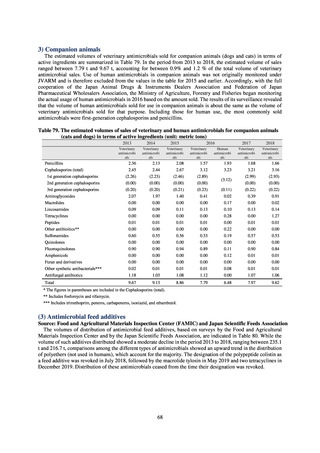
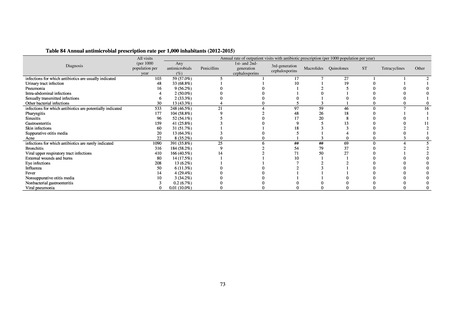
(7) Monitoring on the antimicrobial-resistant Campylobacter spp. isolated from humans
1) Overview
Currently the monitoring regarding the emergence of antimicrobial-resistant Campylobacter spp. derived from humans
is undertaken as research activities by the Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Public Health, as part of the food safety assurance
and promotion research project, with grants for research from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan.[9]
2) Survey methods
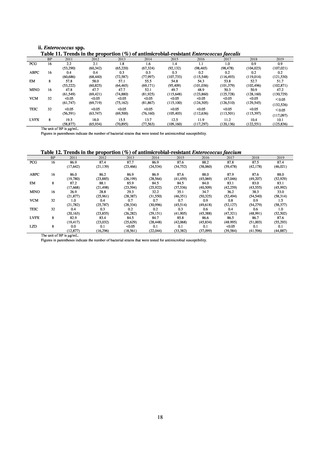
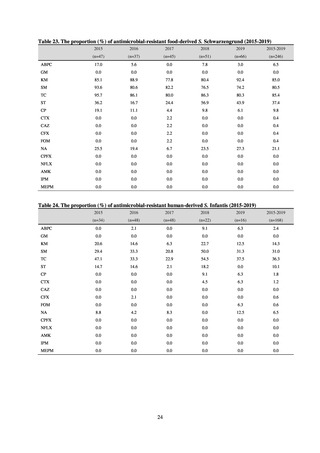
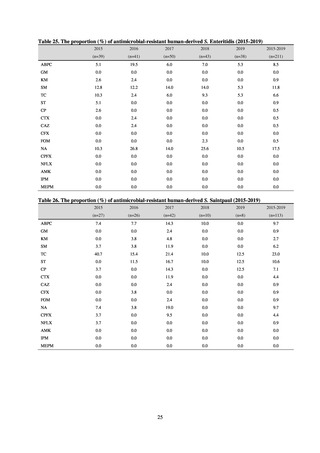
Antimicrobial susceptibility tests were conducted by the disk method, in accordance with the CLSI standards in US.[9]
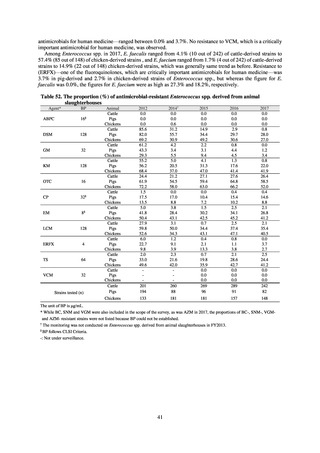
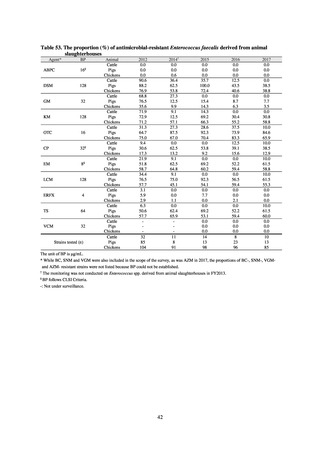
The 110 C. jejuni strains and 8 C. coli strains that were isolated from the stool of diarrhea cases at hospitals in Tokyo in
2018 were tested using antimicrobials such as TC, NA, CPFX, norfloxacin (NFLX), ofloxacin (OFLX), and EM.
3) Prospects
To identify the emergence of antimicrobial-resistant C. jejuni /C. coli on a wide-area basis, it is required to standardize
tested antimicrobials, implementation methods, assessment criteria, and other details. While tests were conducted using the
disk method, in accordance with U.S. CLSI standards, judgment criteria are provided for only three agents, namely CPFX
and EM. Accordingly, other agents were assessed in accordance with standards unified as part of a Ministry of Health,
Labour and Welfare-funded research project concerning the promotion of food safety, with reference to EUCAST
breakpoints and various literature. It is required to conduct antimicrobial susceptibility tests using common methods not
only for strains isolated from humans, but also for strains isolated from food, in order to know the emergence of
antimicrobial-resistant bacteria nationwide.
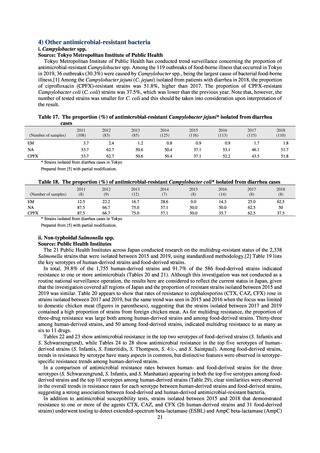
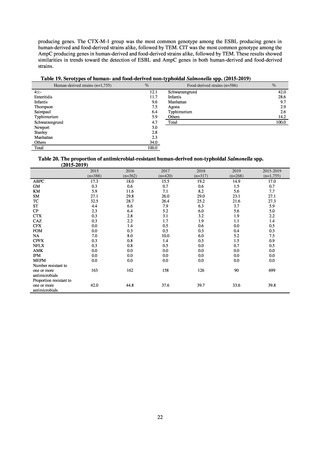
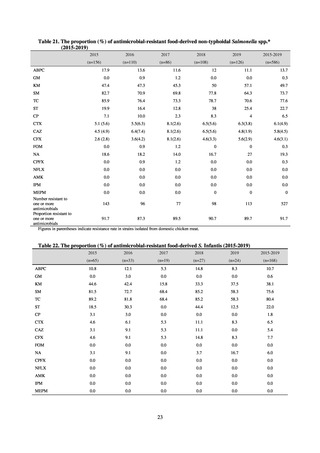
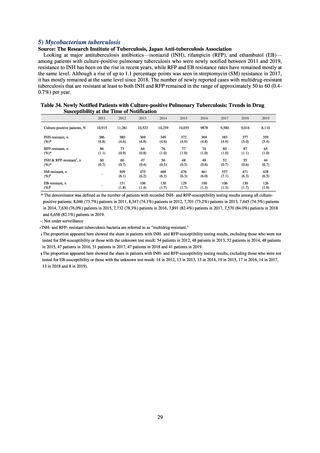
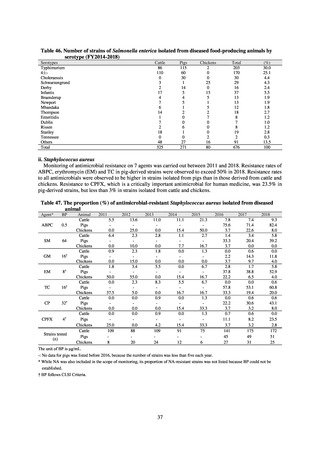
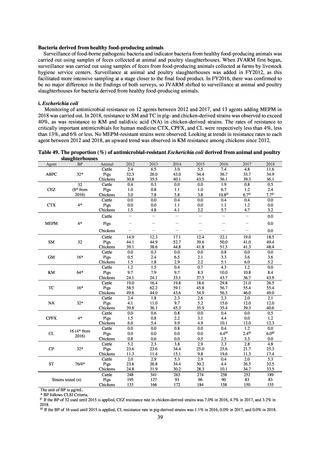
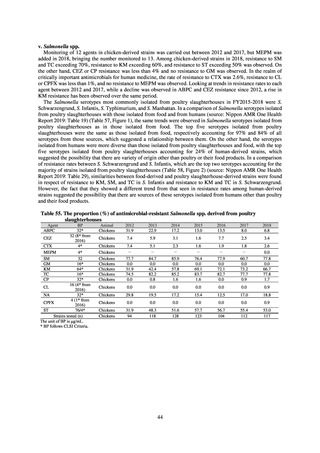
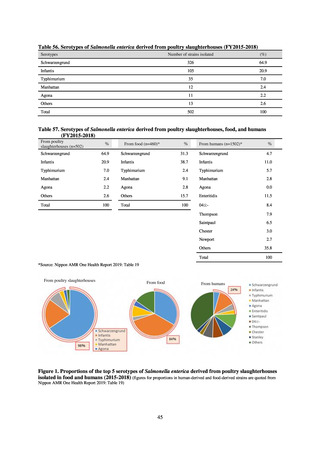
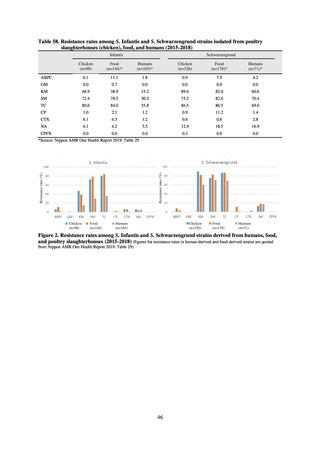
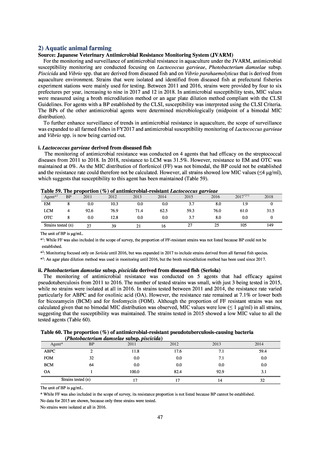
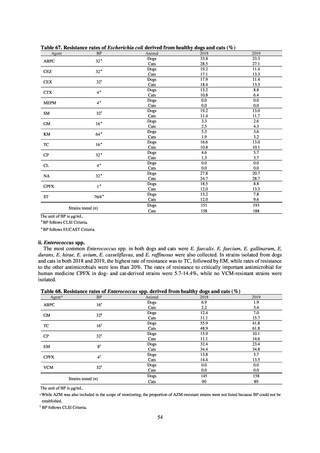
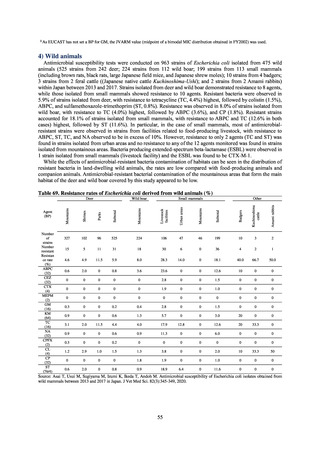
(8) Monitoring on the antimicrobial-resistant non-typhoidal Salmonella spp. isolated from
humans and from food
1) Overview
Many Public Health Institutes conducted resistance monitoring regarding antimicrobial-resistant bacteria derived from
food. Several Public Health Institutes were organized to undertake the monitoring of antimicrobial-resistant bacteria
derived from food as research activities, as part of the food safety assurance and promotion research project, with Grants
for research from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan.[10] This is likely the first monitoring in Japan
regarding antimicrobial-resistant bacteria derived from food on a nationwide scale, conducted by standardized methods.
The collected data were also reported to GLASS, which was launched by WHO.
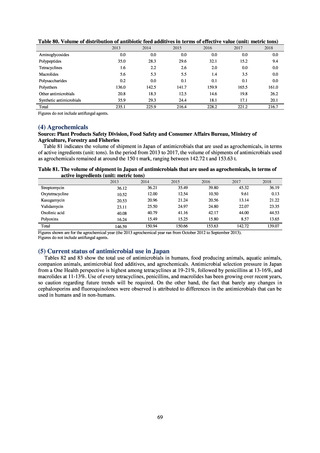
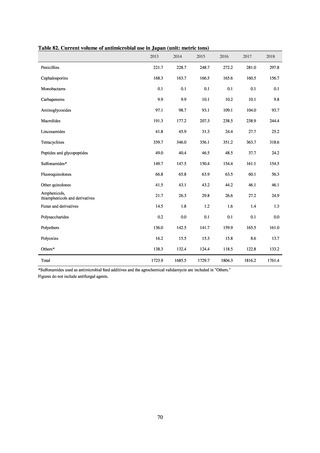
2) Methods
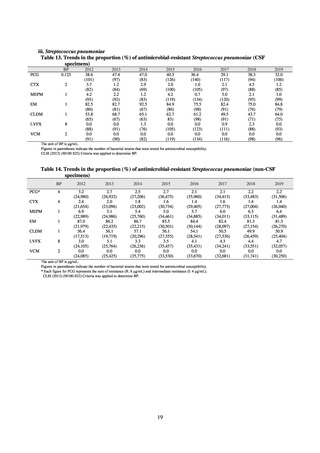
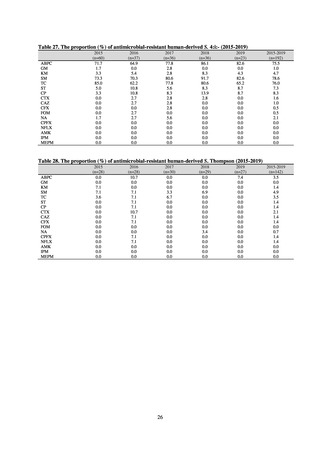
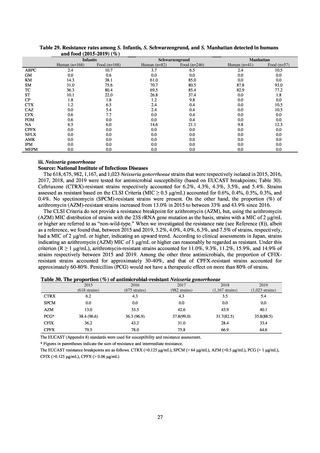
With cooperation from 21 Public Health Institutes across Japan, an antimicrobial resistance monitoring was conducted
using the common protocol, antimicrobials, instruments, etc., concerning bacteria, particularly Salmonella spp., derived
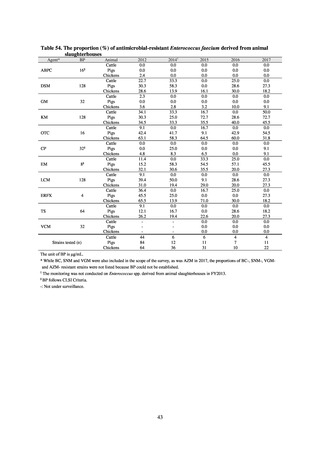
from human patients and from food, as collected by these Public Health Institutes.[10] The monitoring was targeted at
Salmonella spp. strains that were isolated from human patients and from food in 2015 and 2019. Strains derived from
humans included those isolated from specimens of patients with infectious gastroenteritis or with food poisoning. For each
strain derived from food, the type of source food and the date of isolation were identified. When the source food was
chicken meat, information was collected concerning the country of production (domestic, imported (country name), and
unknown). The 21 cooperating Public Health Institutes performed antimicrobial susceptibility tests by the CLSI disk
diffusion method, in accordance with the Public Health Institute Group Protocol for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests,
using strains that were assessed as Salmonella spp. All Public Health Institutes used common reagents (e.g. susceptibility
disks) and instruments (e.g. disk dispensers, vernier calipers) for the tests. Susceptibility disks were laid out on an agar
plate as indicated in the layout drawing in the protocol, so that inhibition circles would not be coalesced. The diameters of
inhibition circles were measured, and the measurements were assessed based on the susceptibility assessment chart in the
protocol.
97
The establishment of Japan’s first AMU surveillance programs in the form of JAMUS and J-SIPHE put in place a system
that enables trends in AMU over time to be fed back to the public. While sources of AMU information include both data
on the volume of sales and insurance billing data, this report focuses on sales data. This is because: 1) it is an international
standard; 2) using different sources of information to show information for the same purpose, namely AMU, will confuse
the reader; and 3) the outcome indices in the National Action Plan on AMR are based on the results of surveillance of sales
volumes. The sources of information used and the way in which they are presented need to be altered according to their
purpose and further consideration is required regarding the form in which they should be collated and fed back on an
ongoing basis.
(7) Monitoring on the antimicrobial-resistant Campylobacter spp. isolated from humans
1) Overview
Currently the monitoring regarding the emergence of antimicrobial-resistant Campylobacter spp. derived from humans
is undertaken as research activities by the Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Public Health, as part of the food safety assurance
and promotion research project, with grants for research from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan.[9]
2) Survey methods
Antimicrobial susceptibility tests were conducted by the disk method, in accordance with the CLSI standards in US.[9]
The 110 C. jejuni strains and 8 C. coli strains that were isolated from the stool of diarrhea cases at hospitals in Tokyo in
2018 were tested using antimicrobials such as TC, NA, CPFX, norfloxacin (NFLX), ofloxacin (OFLX), and EM.
3) Prospects
To identify the emergence of antimicrobial-resistant C. jejuni /C. coli on a wide-area basis, it is required to standardize
tested antimicrobials, implementation methods, assessment criteria, and other details. While tests were conducted using the
disk method, in accordance with U.S. CLSI standards, judgment criteria are provided for only three agents, namely CPFX
and EM. Accordingly, other agents were assessed in accordance with standards unified as part of a Ministry of Health,
Labour and Welfare-funded research project concerning the promotion of food safety, with reference to EUCAST
breakpoints and various literature. It is required to conduct antimicrobial susceptibility tests using common methods not
only for strains isolated from humans, but also for strains isolated from food, in order to know the emergence of
antimicrobial-resistant bacteria nationwide.
(8) Monitoring on the antimicrobial-resistant non-typhoidal Salmonella spp. isolated from
humans and from food
1) Overview
Many Public Health Institutes conducted resistance monitoring regarding antimicrobial-resistant bacteria derived from
food. Several Public Health Institutes were organized to undertake the monitoring of antimicrobial-resistant bacteria
derived from food as research activities, as part of the food safety assurance and promotion research project, with Grants
for research from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan.[10] This is likely the first monitoring in Japan
regarding antimicrobial-resistant bacteria derived from food on a nationwide scale, conducted by standardized methods.
The collected data were also reported to GLASS, which was launched by WHO.
2) Methods
With cooperation from 21 Public Health Institutes across Japan, an antimicrobial resistance monitoring was conducted
using the common protocol, antimicrobials, instruments, etc., concerning bacteria, particularly Salmonella spp., derived
from human patients and from food, as collected by these Public Health Institutes.[10] The monitoring was targeted at
Salmonella spp. strains that were isolated from human patients and from food in 2015 and 2019. Strains derived from
humans included those isolated from specimens of patients with infectious gastroenteritis or with food poisoning. For each
strain derived from food, the type of source food and the date of isolation were identified. When the source food was
chicken meat, information was collected concerning the country of production (domestic, imported (country name), and
unknown). The 21 cooperating Public Health Institutes performed antimicrobial susceptibility tests by the CLSI disk
diffusion method, in accordance with the Public Health Institute Group Protocol for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests,
using strains that were assessed as Salmonella spp. All Public Health Institutes used common reagents (e.g. susceptibility
disks) and instruments (e.g. disk dispensers, vernier calipers) for the tests. Susceptibility disks were laid out on an agar
plate as indicated in the layout drawing in the protocol, so that inhibition circles would not be coalesced. The diameters of
inhibition circles were measured, and the measurements were assessed based on the susceptibility assessment chart in the
protocol.
97