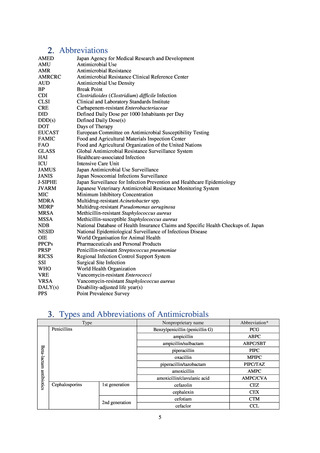
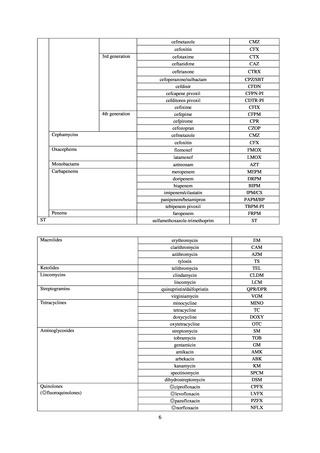
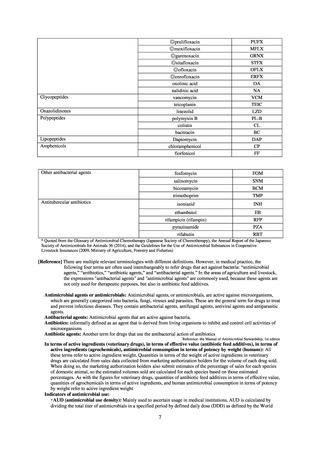
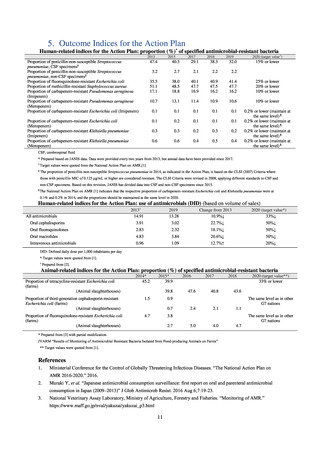
よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
【参考資料3】【英版R4.1.17】Nippon AMR One Health Report (NAOR) 2020 (32 ページ)
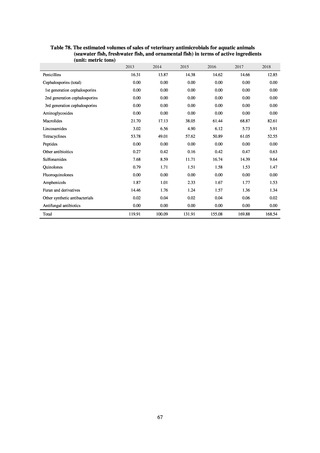
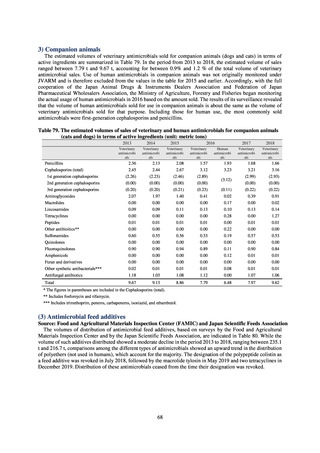
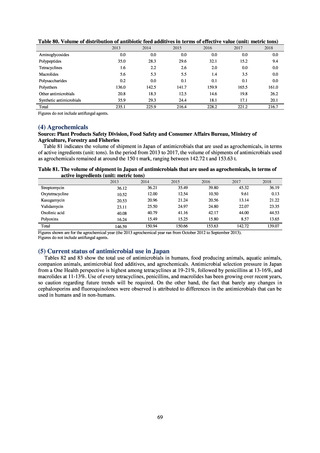
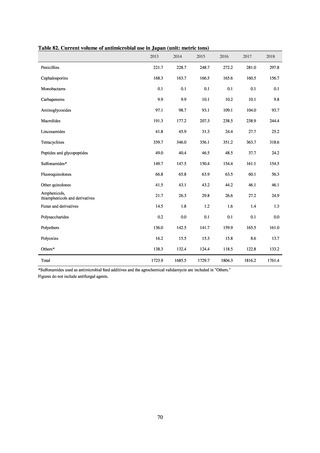
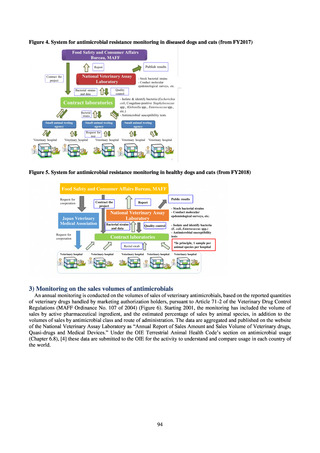
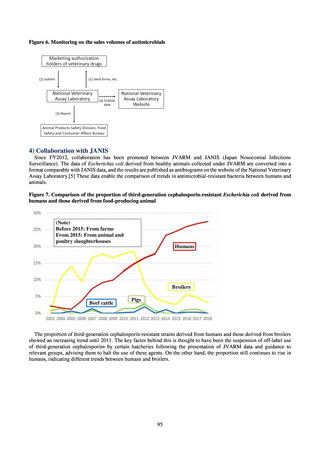
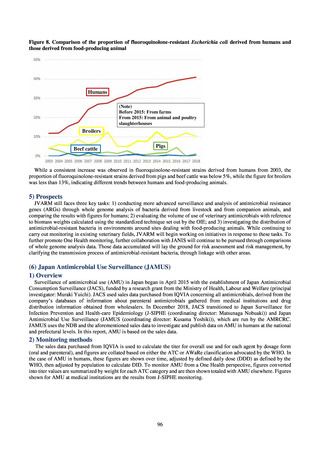
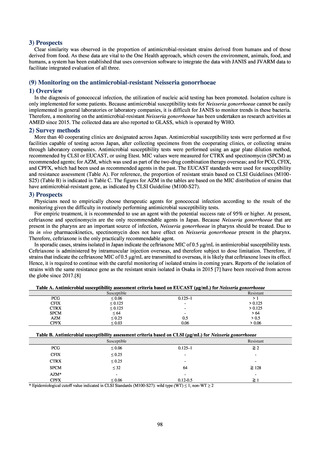
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_23261.html |
| 出典情報 | 国際的に脅威となる感染症対策関係閣僚会議 薬剤耐性ワンヘルス動向調査検討会(第9回 1/17)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
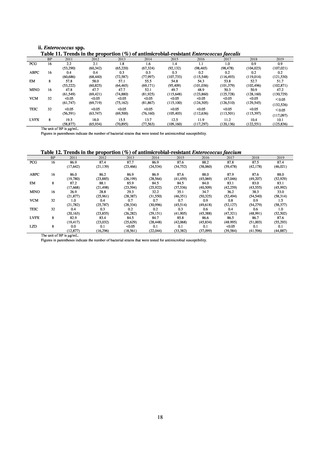
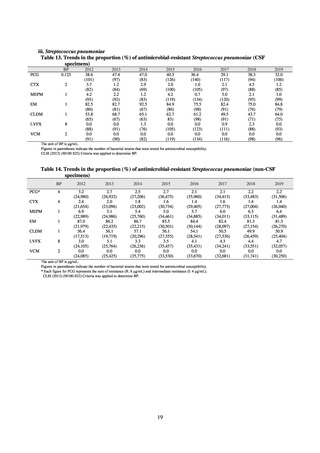
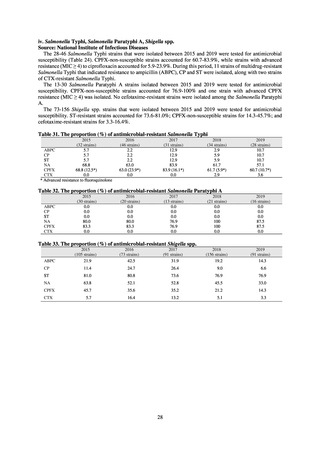
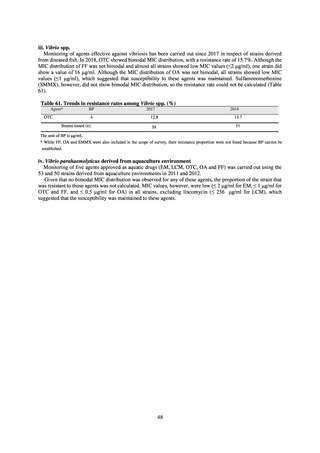
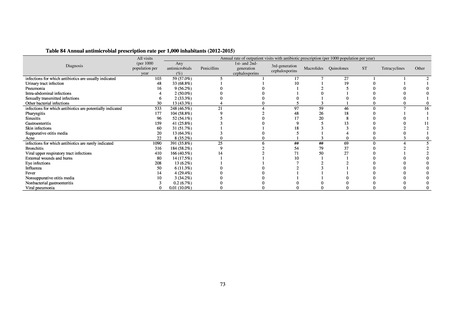
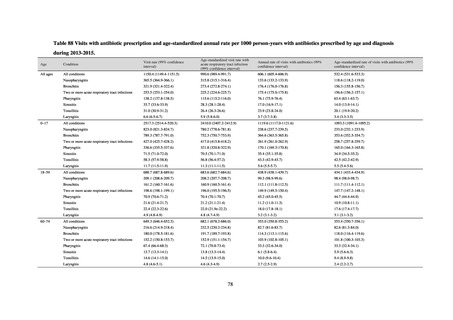
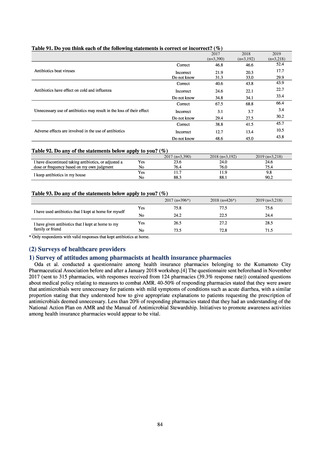
ii. Infections at Intensive Care Unit (ICU)
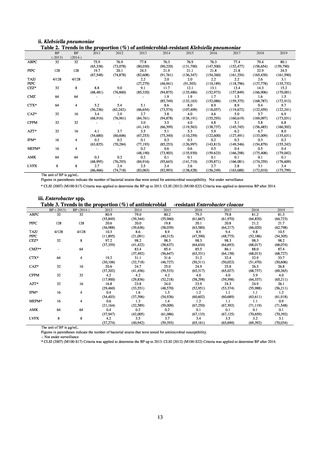
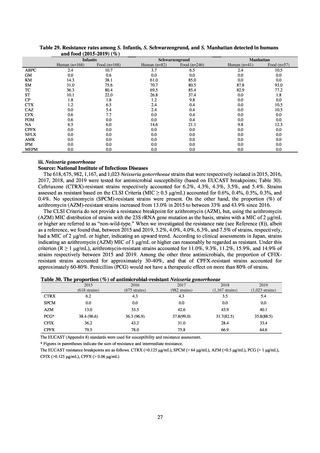
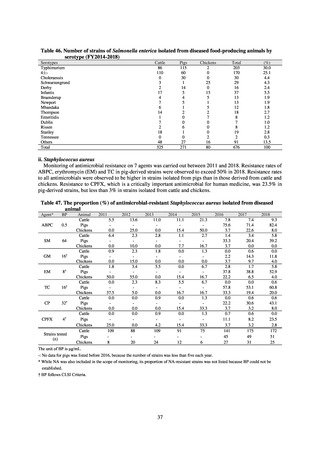
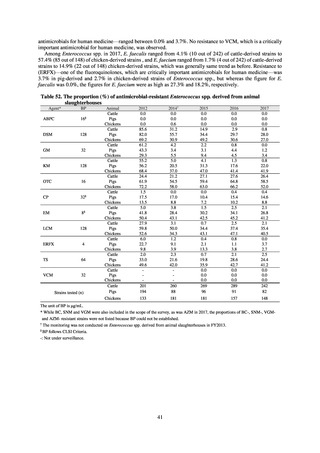
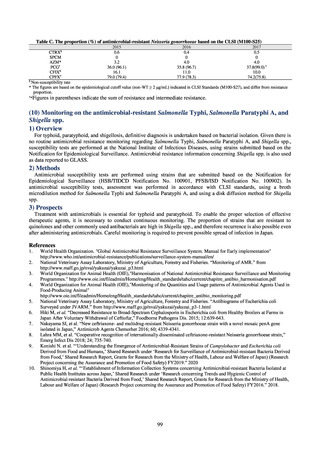
Table 36. Incidence rates of infection at ICU
Ventilatorassociated
pneumonia
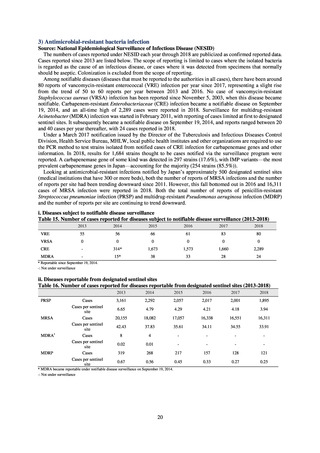
Urinary tract
infection
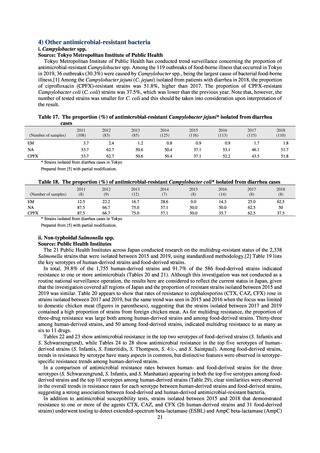
Catheterrelated
bloodstream
infection
Total infection incidence
rate*
Total infections at monitored
medical institutions
Total infection incidence
rate*
Total infections at monitored
medical institutions
Total infection incidence
rate*
Total infections at monitored
medical institutions
2011
2012
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
2018
1.7
1.4
1.3
1.4
1.5
1.5
1.3
1.3
382
327
324
395
522
499
405
409
0.5
0.5
0.6
0.5
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
111
124
143
148
190
219
213
244
0.7
0.7
0.8
0.7
0.7
0.8
0.7
0.6
168
162
204
205
240
263
213
190
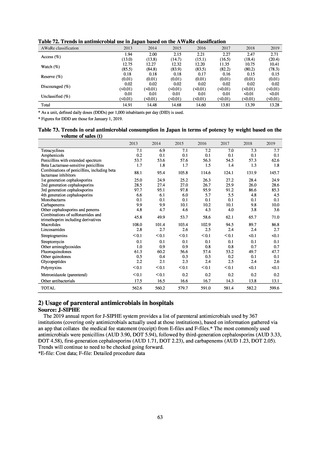
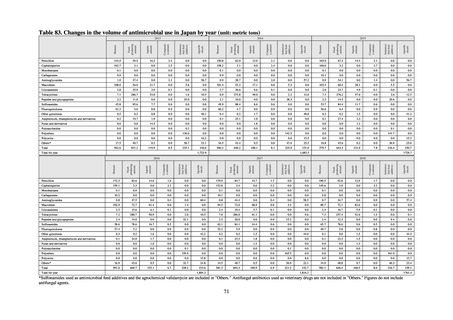
* Total infection incidence rate = (Total infections among applicable patients at medial facilities participated in JANIS) / (Total days of ICU
stay of applicable patients medial facilities participated in JANIS) times 1000
Prepared from annual reports of the ICU division, JANIS.[8]
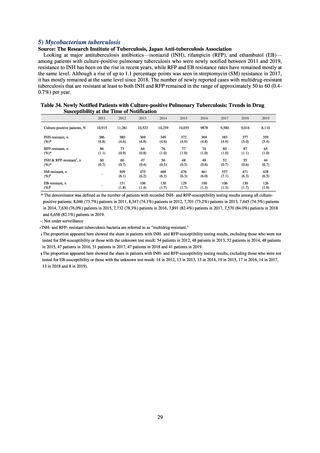
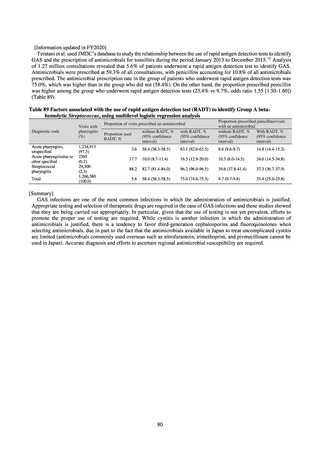
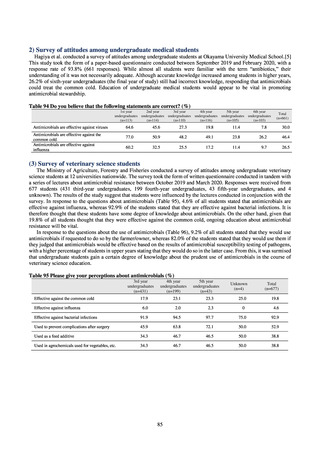
8) Survey of infection treatment and control and the disease burden at hospitals
Source: J-SIPHE, AMR Clinical Reference Center (AMRCRC)
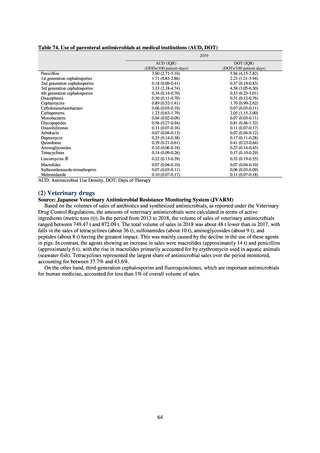
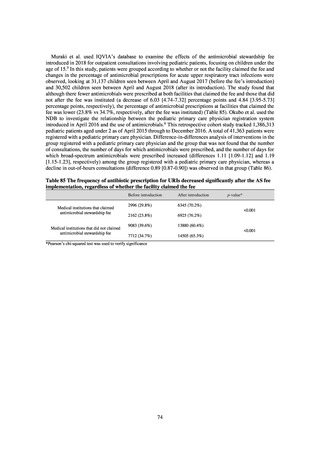
The AMR Clinical Reference Center (AMRCRC) operates the J-SIPHE system, which can be used for AMR
measures at hospitals as well as for promoting regional cooperation. The J-SIPHE 2019 Annual Report covers a
total of 581 participating medical institutions (449 calculating Infection Prevention and Control Premium 1, 127
calculating Infection Prevention and Control Premium 2, and 5 calculating no premium). The median number of
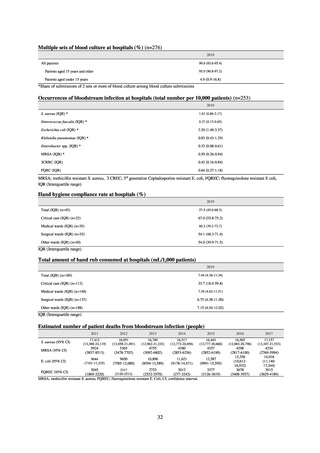
blood cultures submitted at hospitals (n=255) was 23.8/1,000 patients/day (QR: 11.0-34.7), while the median share
of multiple sets of blood culture among adults exceeded 90%. The median positive rate of blood culture was within
an appropriate indicator range at 13.27 (IQR:11.1-17.2). Consideration needs to be given to the hospitals
calculating Infection Prevention and Control Premium 1 forming the majority and the variations in practice
between one hospital and another, but overall the results are good.
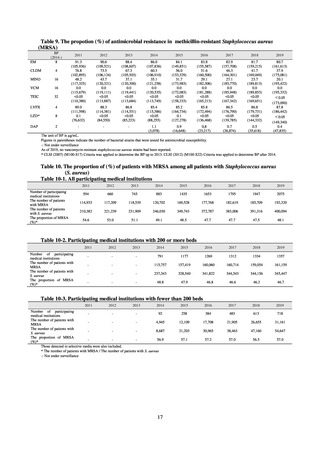
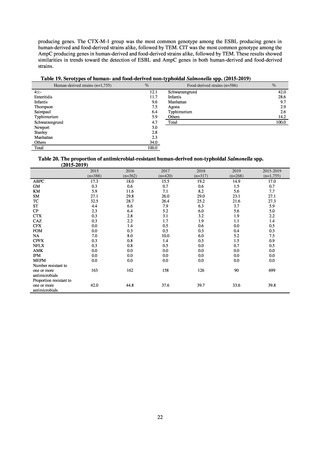
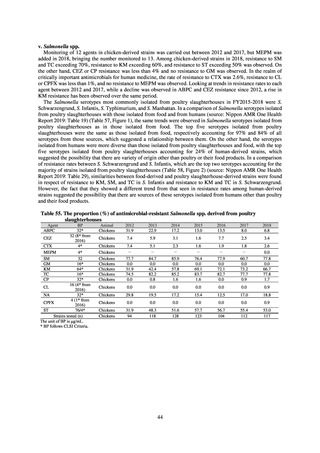
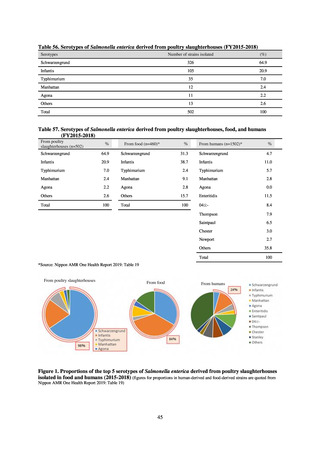
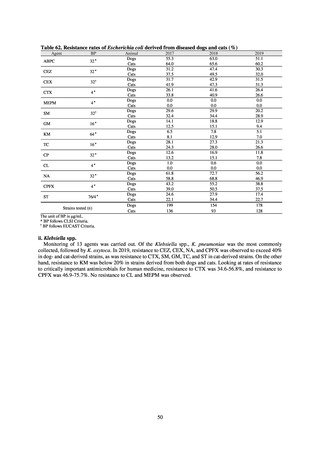
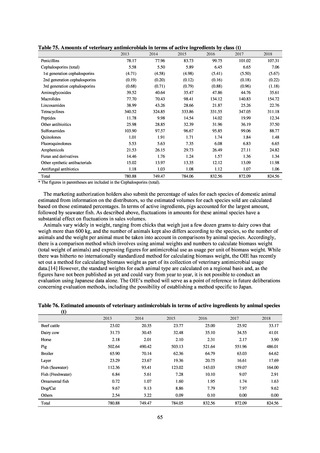
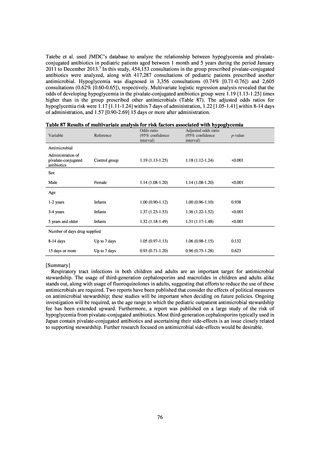
Looking at occurrences of bloodstream infection, Escherichia coli accounted for the highest number, at a total
of 2.20/10,000 patients, followed by S. aureus at a total of 1.61/10,000 patients, and Klebsiella pneumoniae at a
total of 0.83/10,000 patients. It would be desirable for infection control measures to primarily target the bacteria
accounting for the highest percentages of severe infection.
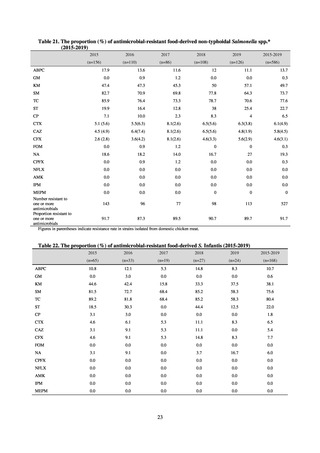
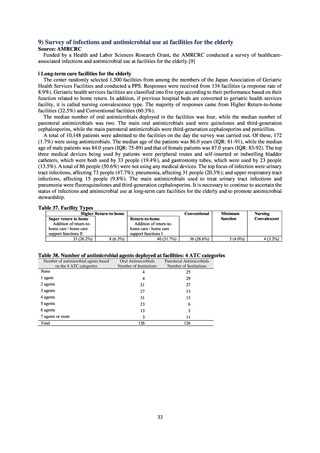
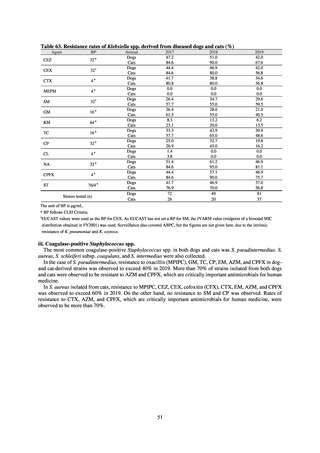
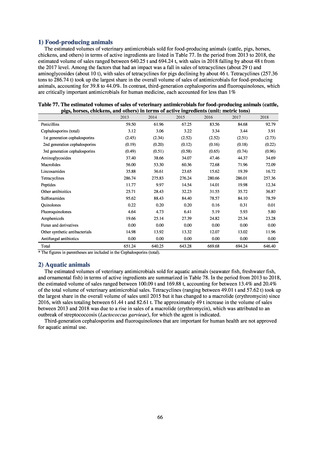
The overall hand hygiene compliance rate was 57.5%, while the breakdown of the figures by ward function
showed that critical care wards had the highest rate of compliance, at 67.0%. The total amount of hand rub
consumed was 7.44 mL/1,000 patients overall, while the breakdown of the figures by ward function showed that
critical care wards used the most, at 33.7 mL/1,000 patients. Further improvements in hand hygiene practice would
be desirable to achieve a hand hygiene compliance target of 70-80%. On the other hand, at facilities with few
infection control resources, monitoring of infection control over time would be desirable, using the amount of
hand rub consumed as a simple alternative indicator.
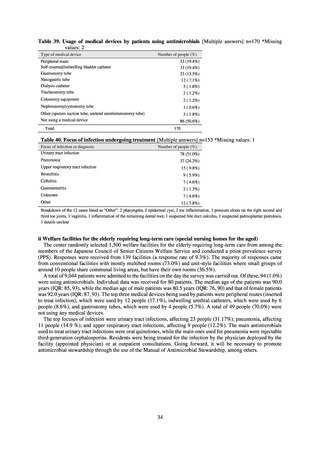
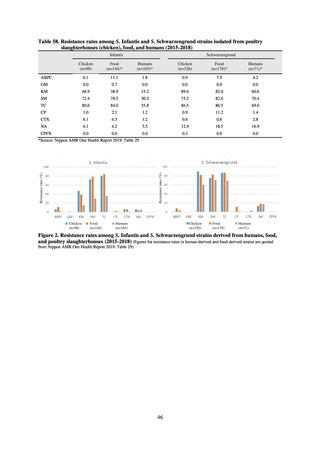
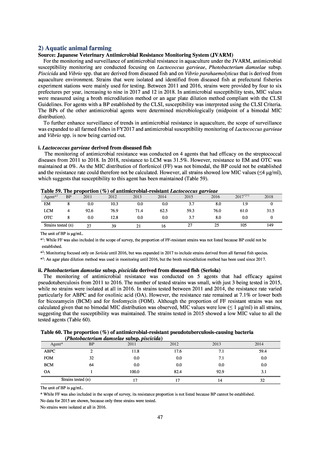
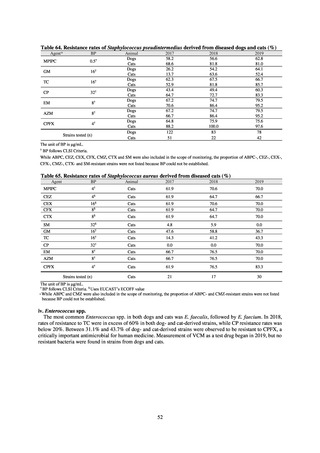
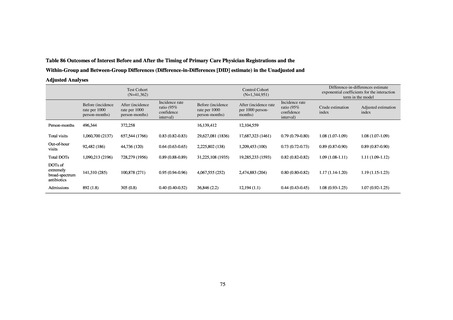
The estimated number of deaths in patients with bloodstream infections was published after a study of JANIS
data carried out with a Health and Labor Sciences Research Grant. The number of deaths due to MRSA has been
declining by the year and was estimated to have reached 4,224 in 2017, while the number of deaths due to
fluoroquinolone-resistant Escherichia coli has been on the rise and was estimated at 3,915 in 2017. Research into
the disease burden of AMR will continue, with the goal of increasing the number of bacterial strains covered over
time and ultimately calculating disability-adjusted life years (DALYs).
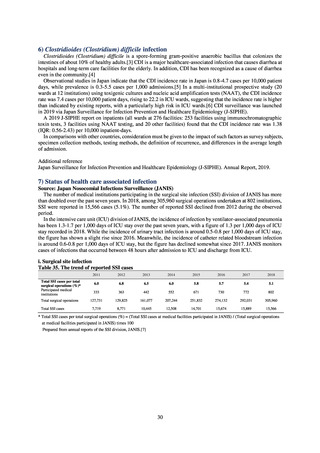
Basic information on medical institutions participating in J-SIPHE
2019
Number of beds (IQR)
340.5 (221.3-525.3)
Average length of hospital stay (IQR)
13.6 (11.7-17.1)
QR (Interquartile range)
31
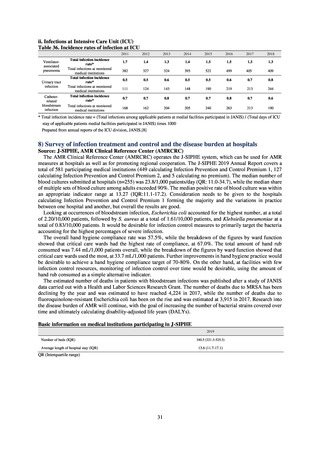
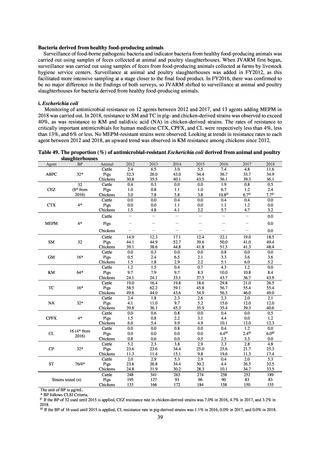
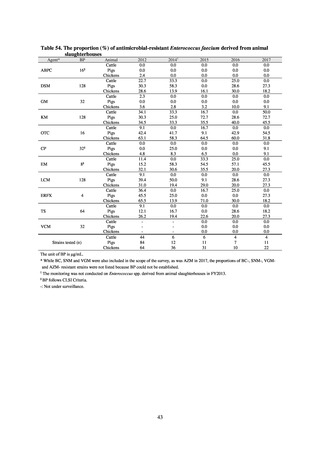
Table 36. Incidence rates of infection at ICU
Ventilatorassociated
pneumonia
Urinary tract
infection
Catheterrelated
bloodstream
infection
Total infection incidence
rate*
Total infections at monitored
medical institutions
Total infection incidence
rate*
Total infections at monitored
medical institutions
Total infection incidence
rate*
Total infections at monitored
medical institutions
2011
2012
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
2018
1.7
1.4
1.3
1.4
1.5
1.5
1.3
1.3
382
327
324
395
522
499
405
409
0.5
0.5
0.6
0.5
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
111
124
143
148
190
219
213
244
0.7
0.7
0.8
0.7
0.7
0.8
0.7
0.6
168
162
204
205
240
263
213
190
* Total infection incidence rate = (Total infections among applicable patients at medial facilities participated in JANIS) / (Total days of ICU
stay of applicable patients medial facilities participated in JANIS) times 1000
Prepared from annual reports of the ICU division, JANIS.[8]
8) Survey of infection treatment and control and the disease burden at hospitals
Source: J-SIPHE, AMR Clinical Reference Center (AMRCRC)
The AMR Clinical Reference Center (AMRCRC) operates the J-SIPHE system, which can be used for AMR
measures at hospitals as well as for promoting regional cooperation. The J-SIPHE 2019 Annual Report covers a
total of 581 participating medical institutions (449 calculating Infection Prevention and Control Premium 1, 127
calculating Infection Prevention and Control Premium 2, and 5 calculating no premium). The median number of
blood cultures submitted at hospitals (n=255) was 23.8/1,000 patients/day (QR: 11.0-34.7), while the median share
of multiple sets of blood culture among adults exceeded 90%. The median positive rate of blood culture was within
an appropriate indicator range at 13.27 (IQR:11.1-17.2). Consideration needs to be given to the hospitals
calculating Infection Prevention and Control Premium 1 forming the majority and the variations in practice
between one hospital and another, but overall the results are good.
Looking at occurrences of bloodstream infection, Escherichia coli accounted for the highest number, at a total
of 2.20/10,000 patients, followed by S. aureus at a total of 1.61/10,000 patients, and Klebsiella pneumoniae at a
total of 0.83/10,000 patients. It would be desirable for infection control measures to primarily target the bacteria
accounting for the highest percentages of severe infection.
The overall hand hygiene compliance rate was 57.5%, while the breakdown of the figures by ward function
showed that critical care wards had the highest rate of compliance, at 67.0%. The total amount of hand rub
consumed was 7.44 mL/1,000 patients overall, while the breakdown of the figures by ward function showed that
critical care wards used the most, at 33.7 mL/1,000 patients. Further improvements in hand hygiene practice would
be desirable to achieve a hand hygiene compliance target of 70-80%. On the other hand, at facilities with few
infection control resources, monitoring of infection control over time would be desirable, using the amount of
hand rub consumed as a simple alternative indicator.
The estimated number of deaths in patients with bloodstream infections was published after a study of JANIS
data carried out with a Health and Labor Sciences Research Grant. The number of deaths due to MRSA has been
declining by the year and was estimated to have reached 4,224 in 2017, while the number of deaths due to
fluoroquinolone-resistant Escherichia coli has been on the rise and was estimated at 3,915 in 2017. Research into
the disease burden of AMR will continue, with the goal of increasing the number of bacterial strains covered over
time and ultimately calculating disability-adjusted life years (DALYs).
Basic information on medical institutions participating in J-SIPHE
2019
Number of beds (IQR)
340.5 (221.3-525.3)
Average length of hospital stay (IQR)
13.6 (11.7-17.1)
QR (Interquartile range)
31