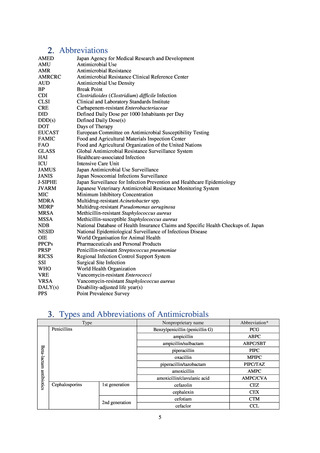
よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
【参考資料3】【英版R4.1.17】Nippon AMR One Health Report (NAOR) 2020 (21 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_23261.html |
| 出典情報 | 国際的に脅威となる感染症対策関係閣僚会議 薬剤耐性ワンヘルス動向調査検討会(第9回 1/17)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
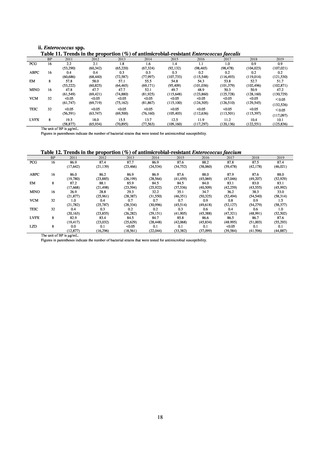
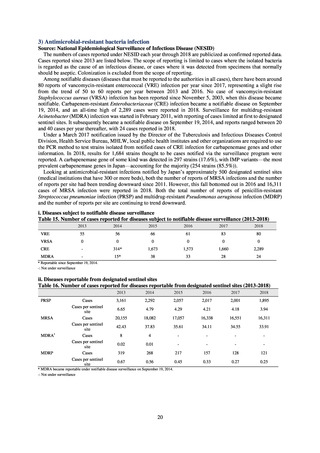
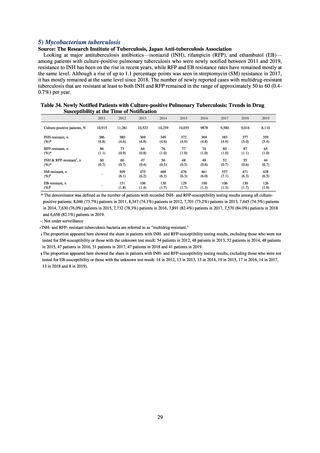
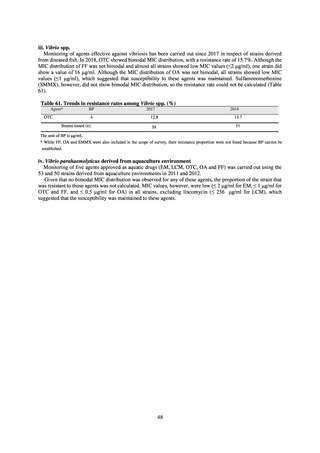
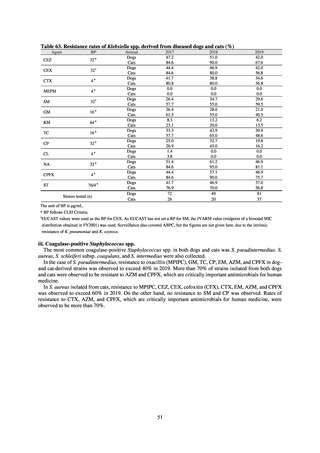
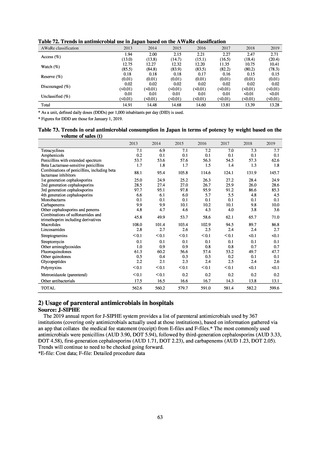
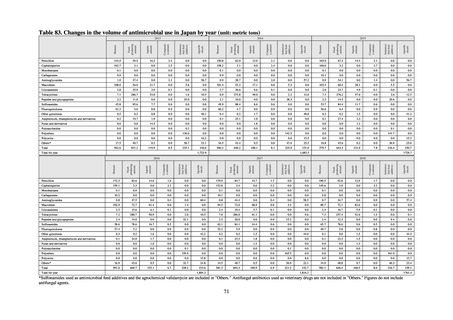
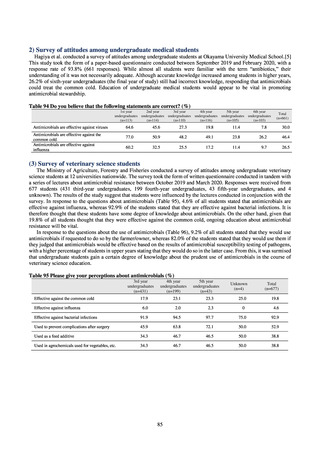
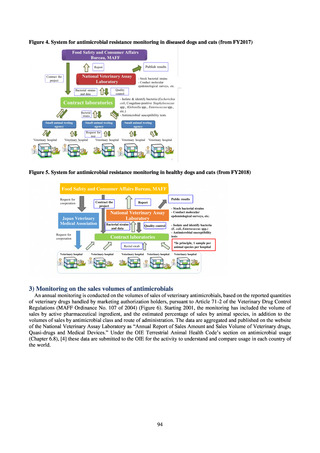
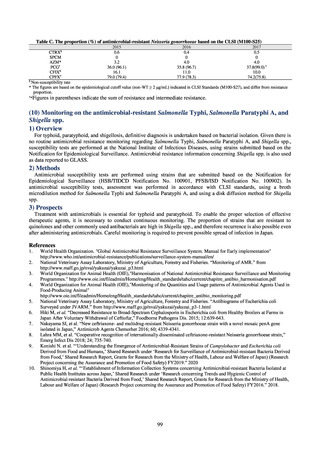
3) Antimicrobial-resistant bacteria infection
Source: National Epidemiological Surveillance of Infectious Disease (NESID)
The numbers of cases reported under NESID each year through 2018 are publicized as confirmed reported data.
Cases reported since 2013 are listed below. The scope of reporting is limited to cases where the isolated bacteria
is regarded as the cause of an infectious disease, or cases where it was detected from specimens that normally
should be aseptic. Colonization is excluded from the scope of reporting.
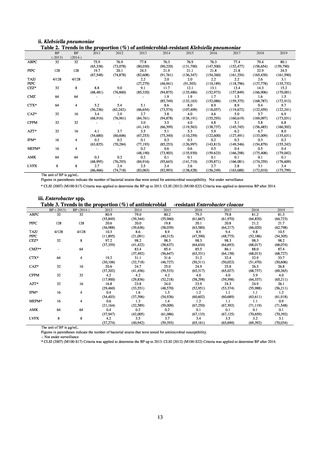
Among notifiable diseases (diseases that must be reported to the authorities in all cases), there have been around
80 reports of vancomycin-resistant enterococcal (VRE) infection per year since 2017, representing a slight rise
from the trend of 50 to 60 reports per year between 2013 and 2016. No case of vancomycin-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus (VRSA) infection has been reported since November 5, 2003, when this disease became
notifiable. Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) infection became a notifiable disease on September
19, 2014, and an all-time high of 2,289 cases were reported in 2018. Surveillance for multidrug-resistant
Acinetobacter (MDRA) infection was started in February 2011, with reporting of cases limited at first to designated
sentinel sites. It subsequently became a notifiable disease on September 19, 2014, and reports ranged between 20
and 40 cases per year thereafter, with 24 cases reported in 2018.
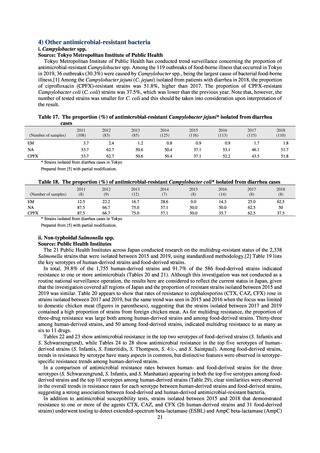
Under a March 2017 notification issued by the Director of the Tuberculosis and Infectious Diseases Control
Division, Health Service Bureau, MHLW, local public health institutes and other organizations are required to use
the PCR method to test strains isolated from notified cases of CRE infection for carbapenemase genes and other
information. In 2018, results for 1,684 strains thought to be cases notified via the surveillance program were
reported. A carbapenemase gene of some kind was detected in 297 strains (17.6%), with IMP variants—the most
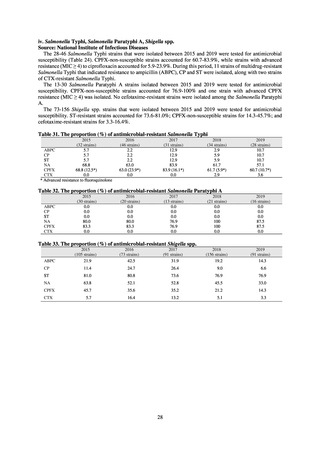
prevalent carbapenemase genes in Japan—accounting for the majority (254 strains (85.5%)).
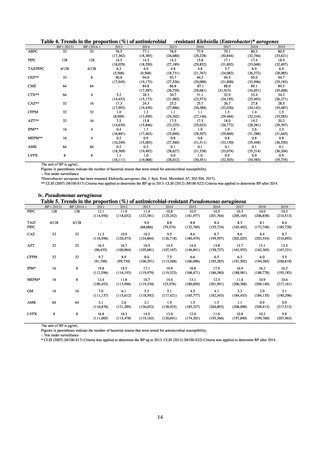
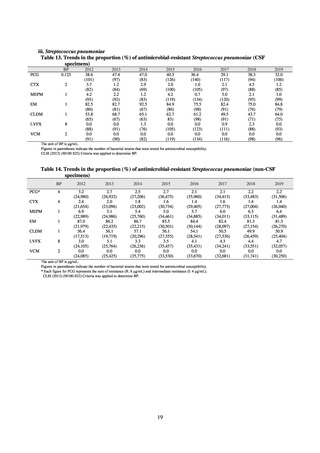
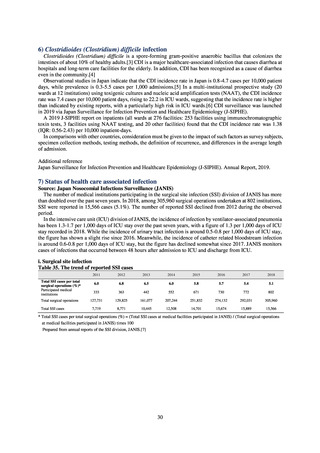
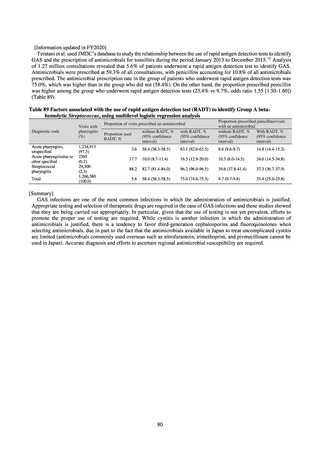
Looking at antimicrobial-resistant infections notified by Japan’s approximately 500 designated sentinel sites
(medical institutions that have 300 or more beds), both the number of reports of MRSA infections and the number
of reports per site had been trending downward since 2011. However, this fall bottomed out in 2016 and 16,311
cases of MRSA infection were reported in 2018. Both the total number of reports of penicillin-resistant
Streptococcus pneumoniae infection (PRSP) and multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection (MDRP)
and the number of reports per site are continuing to trend downward.
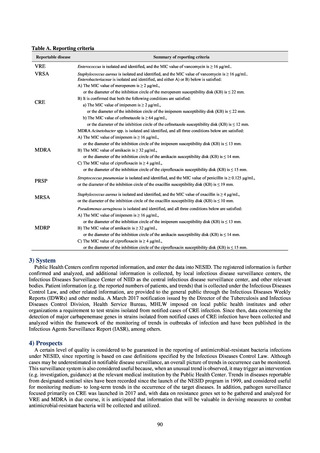
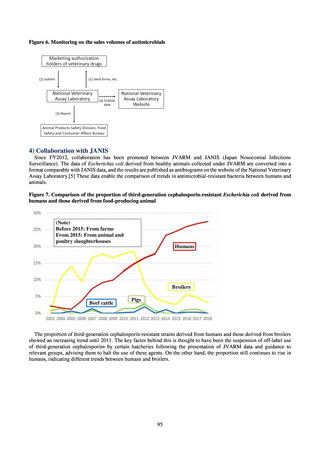
i. Diseases subject to notifiable disease surveillance
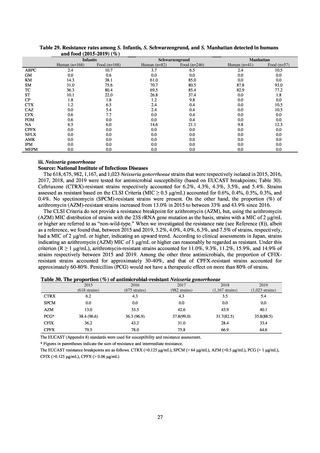
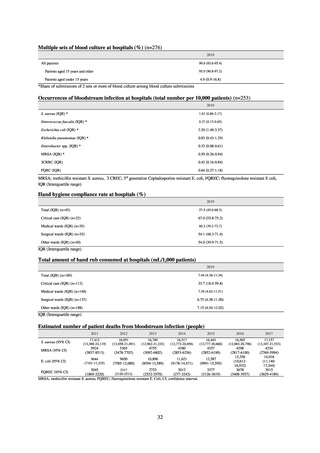
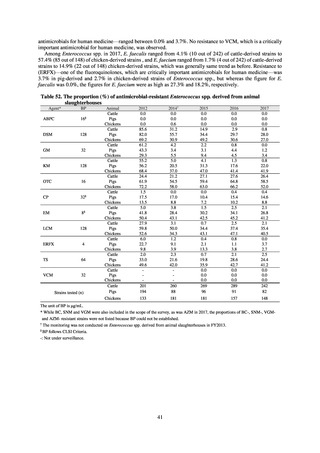
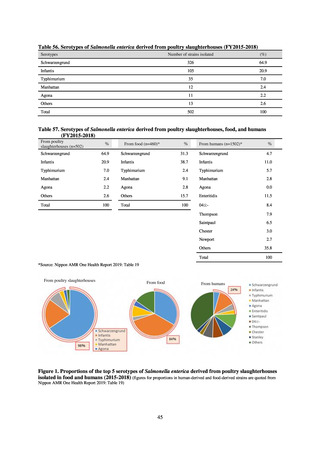
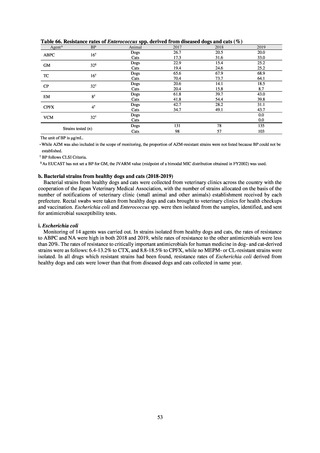
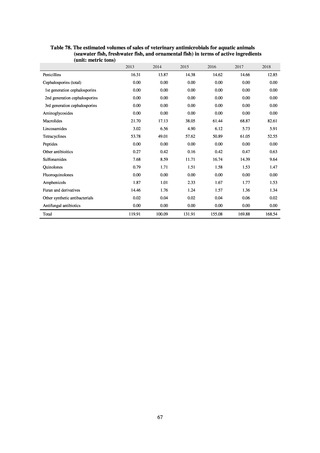
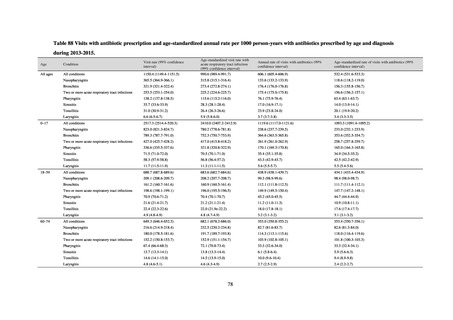
Table 15. Number of cases reported for diseases subject to notifiable disease surveillance (2013-2018)
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
2018
VRE
55
56
66
61
83
80
VRSA
0
0
0
0
0
0
CRE
-
314*
1,673
1,573
1,660
2,289
MDRA
-
15*
38
33
28
24
* Reportable since September 19, 2014.
-: Not under surveillance
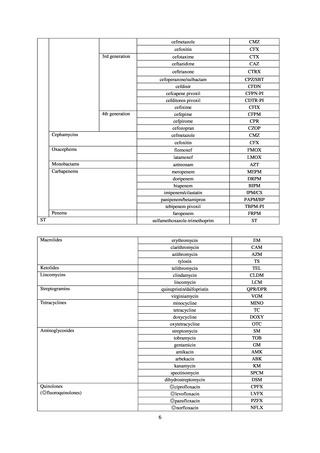
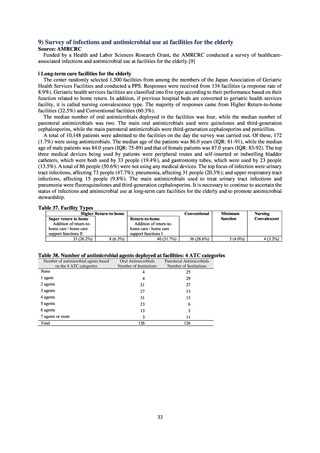
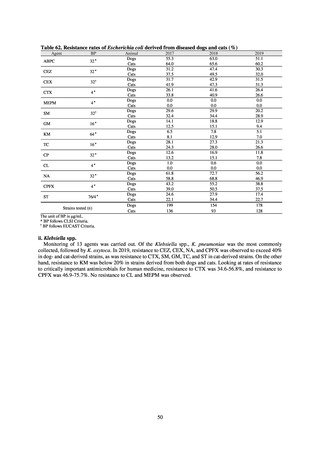
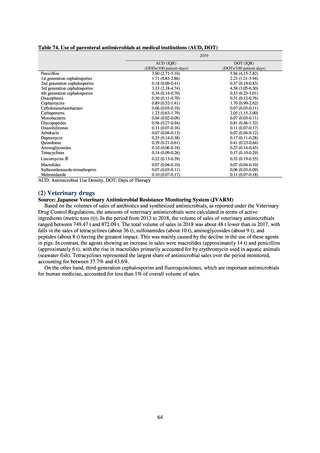
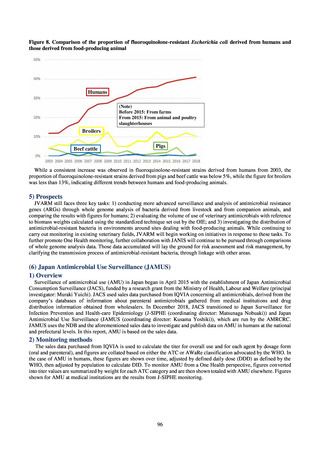
ii. Diseases reportable from designated sentinel sites
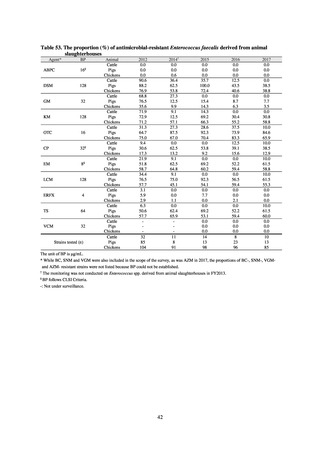
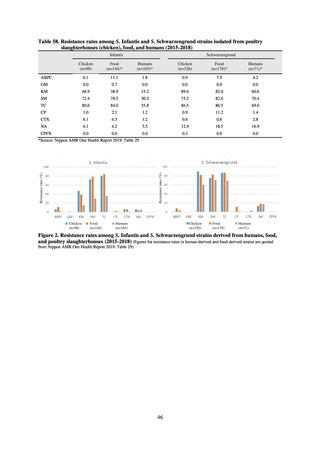
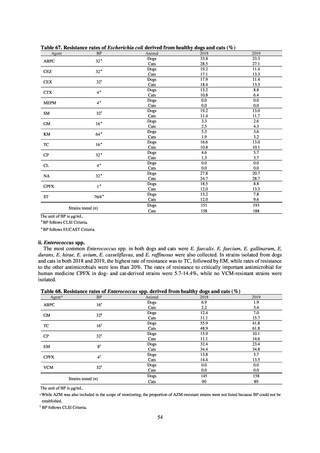
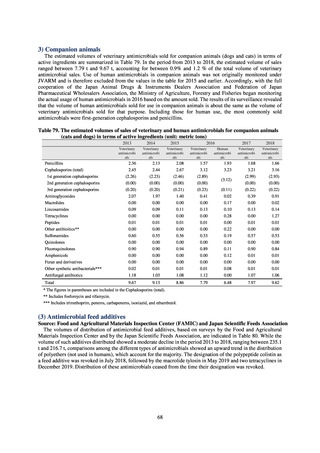
Table 16. Number of cases reported for diseases reportable from designated sentinel sites (2013-2018)
PRSP
MRSA
*
MDRA
MDRP
Cases
Cases per sentinel
site
Cases
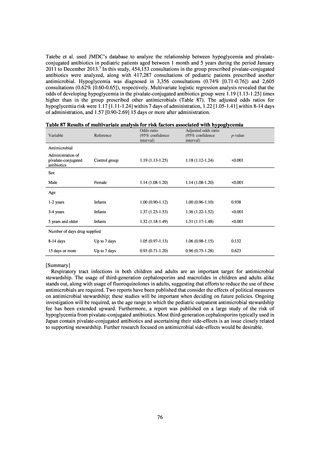
Cases per sentinel
site
Cases
Cases per sentinel
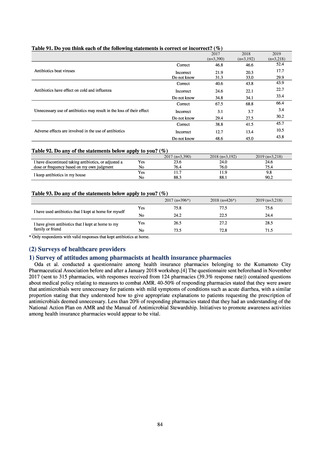
site
Cases
Cases per sentinel
site
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
2018
3,161
2,292
2,057
2,017
2,001
1,895
6.65
4.79
4.29
4.21
4.18
3.94
20,155
18,082
17,057
16,338
16,551
16,311
42.43
37.83
35.61
34.11
34.55
33.91
8
4
-
-
-
-
0.02
0.01
-
-
-
-
319
268
217
157
128
121
0.67
0.56
0.45
0.33
0.27
0.25
* MDRA became reportable under notifiable disease surveillance on September 19, 2014.
-: Not under surveillance
20
Source: National Epidemiological Surveillance of Infectious Disease (NESID)
The numbers of cases reported under NESID each year through 2018 are publicized as confirmed reported data.
Cases reported since 2013 are listed below. The scope of reporting is limited to cases where the isolated bacteria
is regarded as the cause of an infectious disease, or cases where it was detected from specimens that normally
should be aseptic. Colonization is excluded from the scope of reporting.
Among notifiable diseases (diseases that must be reported to the authorities in all cases), there have been around
80 reports of vancomycin-resistant enterococcal (VRE) infection per year since 2017, representing a slight rise
from the trend of 50 to 60 reports per year between 2013 and 2016. No case of vancomycin-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus (VRSA) infection has been reported since November 5, 2003, when this disease became
notifiable. Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) infection became a notifiable disease on September
19, 2014, and an all-time high of 2,289 cases were reported in 2018. Surveillance for multidrug-resistant
Acinetobacter (MDRA) infection was started in February 2011, with reporting of cases limited at first to designated
sentinel sites. It subsequently became a notifiable disease on September 19, 2014, and reports ranged between 20
and 40 cases per year thereafter, with 24 cases reported in 2018.
Under a March 2017 notification issued by the Director of the Tuberculosis and Infectious Diseases Control
Division, Health Service Bureau, MHLW, local public health institutes and other organizations are required to use
the PCR method to test strains isolated from notified cases of CRE infection for carbapenemase genes and other
information. In 2018, results for 1,684 strains thought to be cases notified via the surveillance program were
reported. A carbapenemase gene of some kind was detected in 297 strains (17.6%), with IMP variants—the most
prevalent carbapenemase genes in Japan—accounting for the majority (254 strains (85.5%)).
Looking at antimicrobial-resistant infections notified by Japan’s approximately 500 designated sentinel sites
(medical institutions that have 300 or more beds), both the number of reports of MRSA infections and the number
of reports per site had been trending downward since 2011. However, this fall bottomed out in 2016 and 16,311
cases of MRSA infection were reported in 2018. Both the total number of reports of penicillin-resistant
Streptococcus pneumoniae infection (PRSP) and multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection (MDRP)
and the number of reports per site are continuing to trend downward.
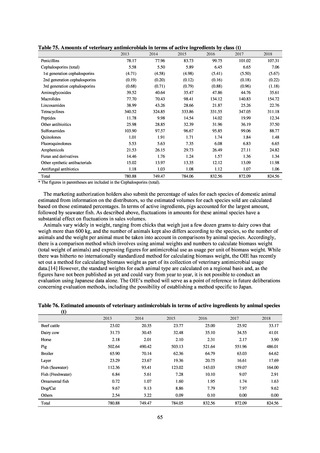
i. Diseases subject to notifiable disease surveillance
Table 15. Number of cases reported for diseases subject to notifiable disease surveillance (2013-2018)
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
2018
VRE
55
56
66
61
83
80
VRSA
0
0
0
0
0
0
CRE
-
314*
1,673
1,573
1,660
2,289
MDRA
-
15*
38
33
28
24
* Reportable since September 19, 2014.
-: Not under surveillance
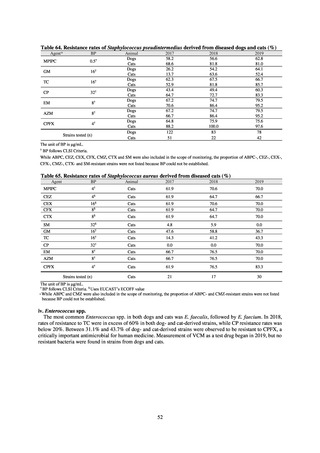
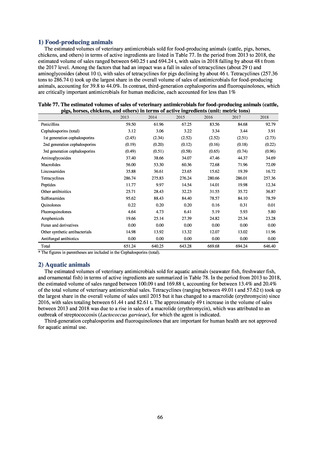
ii. Diseases reportable from designated sentinel sites
Table 16. Number of cases reported for diseases reportable from designated sentinel sites (2013-2018)
PRSP
MRSA
*
MDRA
MDRP
Cases
Cases per sentinel
site
Cases
Cases per sentinel
site
Cases
Cases per sentinel
site
Cases
Cases per sentinel
site
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
2018
3,161
2,292
2,057
2,017
2,001
1,895
6.65
4.79
4.29
4.21
4.18
3.94
20,155
18,082
17,057
16,338
16,551
16,311
42.43
37.83
35.61
34.11
34.55
33.91
8
4
-
-
-
-
0.02
0.01
-
-
-
-
319
268
217
157
128
121
0.67
0.56
0.45
0.33
0.27
0.25
* MDRA became reportable under notifiable disease surveillance on September 19, 2014.
-: Not under surveillance
20