よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
参考資料6_THE ESSENTIALS: CORE COMPETENCIES FOR PROFESSIONAL NURSING EDUCATION (2021 American Association of Colleges of Nursing) (69 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mext.go.jp/b_menu/shingi/chousa/koutou/125/mext_00004.html |
| 出典情報 | 看護学教育モデル・コア・カリキュラムの改訂に関する連絡調整委員会(第1回 7/19)《文部科学省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
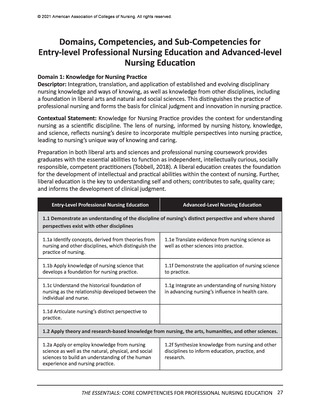
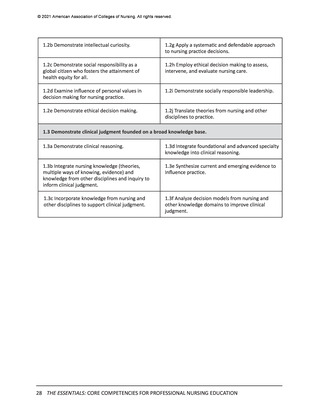
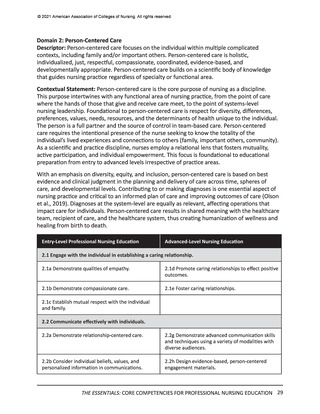
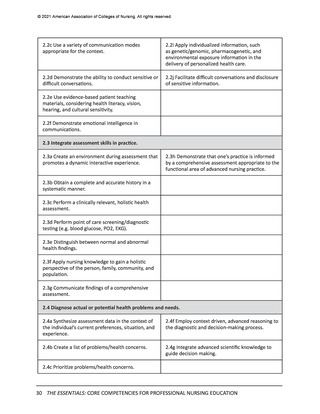
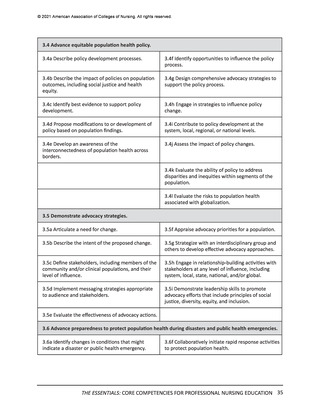
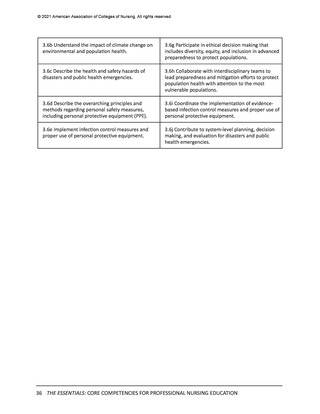
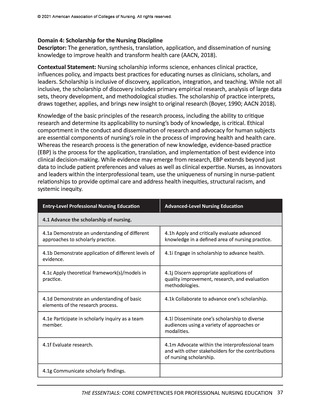
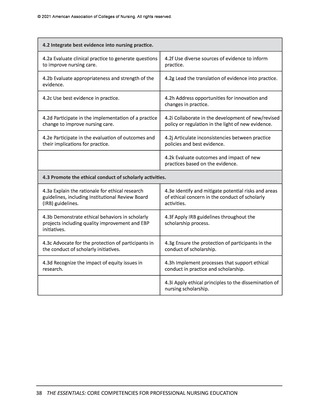
© 2021 American Association of Colleges of Nursing. All rights reserved.
Responsibility: The state or fact of being responsible, answerable, or accountable for something
within one’s power, control, or management.
Return on investment (ROI): A performance measure used to evaluate the efficiency of an
investment or compare the efficiency of a number of different investments. ROI seeks to
directly measure the amount of return on a particular investment, relative to the investment’s
cost. To calculate ROI, the benefit (or return) of an investment is divided by the cost of the
investment. The result is expressed as a percentage or a ratio.
Risk assessment: A process to identify potential hazards and analyze what could happen if a
hazard occurs. To assess risk, organizations often consider possible scenarios that could unfold
and what the potential impacts may be.
Scholarship: The generation, synthesis, translation, application, and dissemination of knowledge
that aims to improve health and transform health care. Scholarship is the communication of
knowledge generated through multiple forms of inquiry that inform clinical practice, nursing
education, policy, and healthcare delivery. Scholarship is inclusive of discovery, integration,
application, and teaching (Boyer, 1990). The hallmark attribute of scholarship is the cumulative
impact of the scholar’s work on the field of nursing and health care.
Self-care: The act of attending to one’s physical or mental health, generally without medical or
other professional consultation.
Self-management: The management of or by oneself; the taking of responsibility for one’s own
behavior and well-being.
Service: is the action of helping or doing work for someone.
Simulation: A technique that creates a situation or environment to allow persons to experience
a representation of a real event for the purpose of practice, learning, evaluation, testing, or to
gain understanding of systems or human actions (AHRQ, 2020).
Social Determinants of Health: See Determinants of Health
Social Justice: The expectation that everyone deserves equal economic, political,
and social rights and opportunities. Equity, access, participation, and human rights are four
principles of social justice including to ensure fair distribution of available resources across
society, to ensure all people have access to goods and services regardless of age, gender, race,
ethnicity etc.; to enable people to participate in decisions that affect their lives, and to protect
individual liberties to information about circumstances and decisions affecting them and to
appeal decisions believed to be unfair (Morgaine, 2014; Nemetchek, 2019).
Social Responsibility: An ethical theory in which individuals are accountable for fulfilling their
civic duty, and the actions of an individual must benefit the whole of society. This typically
involves a balance between economic growth and the welfare of society and the environment.
(Pachchamama Alliance, 2021)
64 THE ESSENTIALS: CORE COMPETENCIES FOR PROFESSIONAL NURSING EDUCATION
Responsibility: The state or fact of being responsible, answerable, or accountable for something
within one’s power, control, or management.
Return on investment (ROI): A performance measure used to evaluate the efficiency of an
investment or compare the efficiency of a number of different investments. ROI seeks to
directly measure the amount of return on a particular investment, relative to the investment’s
cost. To calculate ROI, the benefit (or return) of an investment is divided by the cost of the
investment. The result is expressed as a percentage or a ratio.
Risk assessment: A process to identify potential hazards and analyze what could happen if a
hazard occurs. To assess risk, organizations often consider possible scenarios that could unfold
and what the potential impacts may be.
Scholarship: The generation, synthesis, translation, application, and dissemination of knowledge
that aims to improve health and transform health care. Scholarship is the communication of
knowledge generated through multiple forms of inquiry that inform clinical practice, nursing
education, policy, and healthcare delivery. Scholarship is inclusive of discovery, integration,
application, and teaching (Boyer, 1990). The hallmark attribute of scholarship is the cumulative
impact of the scholar’s work on the field of nursing and health care.
Self-care: The act of attending to one’s physical or mental health, generally without medical or
other professional consultation.
Self-management: The management of or by oneself; the taking of responsibility for one’s own
behavior and well-being.
Service: is the action of helping or doing work for someone.
Simulation: A technique that creates a situation or environment to allow persons to experience
a representation of a real event for the purpose of practice, learning, evaluation, testing, or to
gain understanding of systems or human actions (AHRQ, 2020).
Social Determinants of Health: See Determinants of Health
Social Justice: The expectation that everyone deserves equal economic, political,
and social rights and opportunities. Equity, access, participation, and human rights are four
principles of social justice including to ensure fair distribution of available resources across
society, to ensure all people have access to goods and services regardless of age, gender, race,
ethnicity etc.; to enable people to participate in decisions that affect their lives, and to protect
individual liberties to information about circumstances and decisions affecting them and to
appeal decisions believed to be unfair (Morgaine, 2014; Nemetchek, 2019).
Social Responsibility: An ethical theory in which individuals are accountable for fulfilling their
civic duty, and the actions of an individual must benefit the whole of society. This typically
involves a balance between economic growth and the welfare of society and the environment.
(Pachchamama Alliance, 2021)
64 THE ESSENTIALS: CORE COMPETENCIES FOR PROFESSIONAL NURSING EDUCATION