よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
参考資料6_THE ESSENTIALS: CORE COMPETENCIES FOR PROFESSIONAL NURSING EDUCATION (2021 American Association of Colleges of Nursing) (12 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mext.go.jp/b_menu/shingi/chousa/koutou/125/mext_00004.html |
| 出典情報 | 看護学教育モデル・コア・カリキュラムの改訂に関する連絡調整委員会(第1回 7/19)《文部科学省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
© 2021 American Association of Colleges of Nursing. All rights reserved.
experiences (quality and satisfaction), improving the health of populations, decreasing per
capita costs of health care, and improving care team well-being (Bowles et al., 2018). It is time
for nursing education to refocus and move beyond some long-held beliefs such as: primary care
content is not important because it is not on the national licensing exam for registered nurses;
students only value those skills required in acute care settings; and faculty preceptors only have
limited community-based experiences. Recommendations from the Josiah Macy Foundation
Conference (2016) on expanding the use of registered nursing in primary care provides a call
to education and practice to place more value on primary care as a career choice, effectively
changing the culture of nursing and health care. A collaborative effort between academic and
practice leaders is needed to ensure this culture change and educate primary care practitioners
about the value of the registered nurse role.
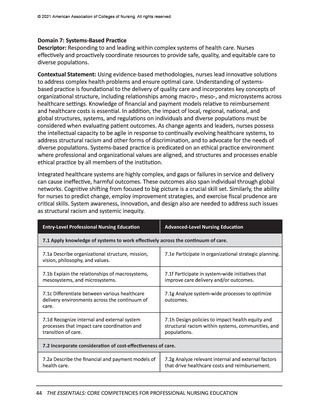
Systems-Based Practice
Integrated healthcare systems that require coordination across settings as well as across the
lifespan of diverse individuals and populations are emerging. Healthcare systems are revising
strategic goals and reorganizing services to move more care from the most expensive venues
– inpatient facilities and emergency departments – to primary care and community settings.
Consequently, nurse employment settings also are shifting, creating a change in workforce
distribution and the requisite knowledge and skills necessary to provide care in those settings.
Knowledge differentiating equity and equality in healthcare systems and systems-based practice
is essential. Nurses in the future are needed to lead initiatives to address structural racism,
systemic inequity, and discrimination. Equitable healthcare better serves the needs of all
individuals, populations, and communities.
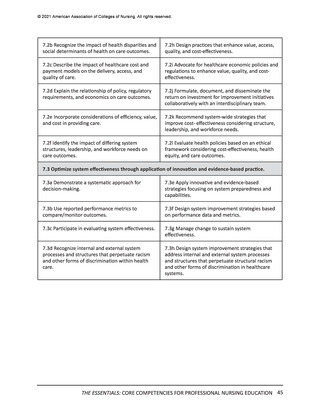
Importantly, an understanding of how local, national, and global structures, systems, politics,
and rules and regulations contribute to the health outcomes of individual patients, populations,
and communities will support students in developing agility and advocacy skills. Factors such as
structural racism, cost containment, resource allocation, and interdisciplinary collaboration are
considered and implemented to ensure the delivery of high quality, equitable, and safe patient
care (Plack et al., 2018).
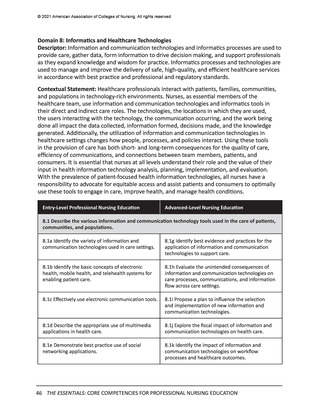
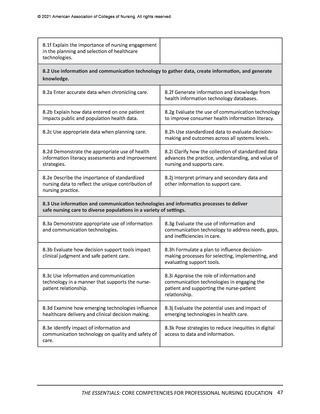
Informatics and Technology
Informatics increasingly has been a focus in nursing education, correlating with the
advancement in sophistication and reach of information technologies, the use of technology to
support healthcare processes and clinical thinking, and the ability of informatics and technology
to positively impact patient outcomes. Health information technology is required for personcentered service across the continuum and requires consistency in user input, proper process,
and quality management. While different specialty roles in nursing may require varying depth
and breadth of informatics competency, basic informatics competencies are foundational to all
nursing practice. Much work will be required to achieve full integration of core information and
communication technologies competencies into nursing curricula.
Engagement and Experience
The future consumers of health care are changing. They are transitioning from passive
participants in medically focused acute care environments to engaged participants of healthcare
services. They actively participate in managing not only their chronic illnesses but also acute
THE ESSENTIALS: CORE COMPETENCIES FOR PROFESSIONAL NURSING EDUCATION
7
experiences (quality and satisfaction), improving the health of populations, decreasing per
capita costs of health care, and improving care team well-being (Bowles et al., 2018). It is time
for nursing education to refocus and move beyond some long-held beliefs such as: primary care
content is not important because it is not on the national licensing exam for registered nurses;
students only value those skills required in acute care settings; and faculty preceptors only have
limited community-based experiences. Recommendations from the Josiah Macy Foundation
Conference (2016) on expanding the use of registered nursing in primary care provides a call
to education and practice to place more value on primary care as a career choice, effectively
changing the culture of nursing and health care. A collaborative effort between academic and
practice leaders is needed to ensure this culture change and educate primary care practitioners
about the value of the registered nurse role.
Systems-Based Practice
Integrated healthcare systems that require coordination across settings as well as across the
lifespan of diverse individuals and populations are emerging. Healthcare systems are revising
strategic goals and reorganizing services to move more care from the most expensive venues
– inpatient facilities and emergency departments – to primary care and community settings.
Consequently, nurse employment settings also are shifting, creating a change in workforce
distribution and the requisite knowledge and skills necessary to provide care in those settings.
Knowledge differentiating equity and equality in healthcare systems and systems-based practice
is essential. Nurses in the future are needed to lead initiatives to address structural racism,
systemic inequity, and discrimination. Equitable healthcare better serves the needs of all
individuals, populations, and communities.
Importantly, an understanding of how local, national, and global structures, systems, politics,
and rules and regulations contribute to the health outcomes of individual patients, populations,
and communities will support students in developing agility and advocacy skills. Factors such as
structural racism, cost containment, resource allocation, and interdisciplinary collaboration are
considered and implemented to ensure the delivery of high quality, equitable, and safe patient
care (Plack et al., 2018).
Informatics and Technology
Informatics increasingly has been a focus in nursing education, correlating with the
advancement in sophistication and reach of information technologies, the use of technology to
support healthcare processes and clinical thinking, and the ability of informatics and technology
to positively impact patient outcomes. Health information technology is required for personcentered service across the continuum and requires consistency in user input, proper process,
and quality management. While different specialty roles in nursing may require varying depth
and breadth of informatics competency, basic informatics competencies are foundational to all
nursing practice. Much work will be required to achieve full integration of core information and
communication technologies competencies into nursing curricula.
Engagement and Experience
The future consumers of health care are changing. They are transitioning from passive
participants in medically focused acute care environments to engaged participants of healthcare
services. They actively participate in managing not only their chronic illnesses but also acute
THE ESSENTIALS: CORE COMPETENCIES FOR PROFESSIONAL NURSING EDUCATION
7