よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
参考資料6_THE ESSENTIALS: CORE COMPETENCIES FOR PROFESSIONAL NURSING EDUCATION (2021 American Association of Colleges of Nursing) (65 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mext.go.jp/b_menu/shingi/chousa/koutou/125/mext_00004.html |
| 出典情報 | 看護学教育モデル・コア・カリキュラムの改訂に関する連絡調整委員会(第1回 7/19)《文部科学省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
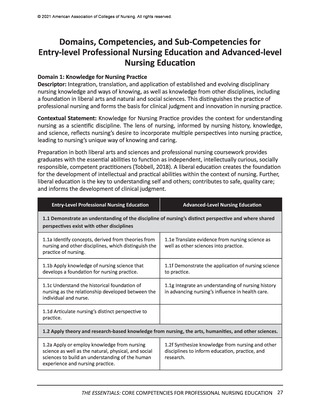
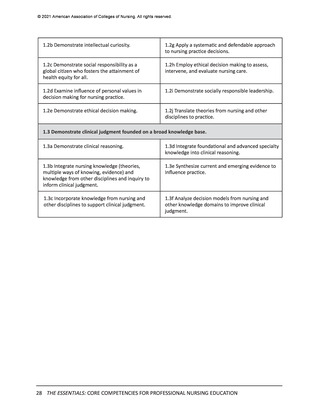
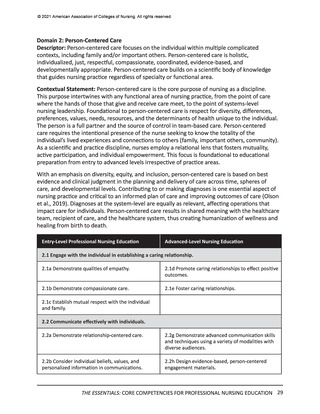
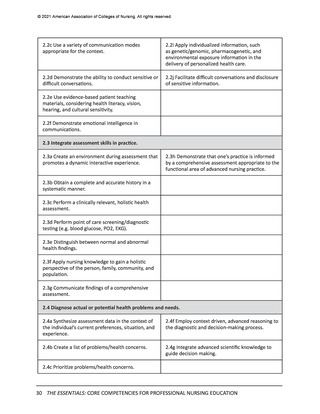
© 2021 American Association of Colleges of Nursing. All rights reserved.
Implicit and unconscious biases: The tendency to process information based on unconscious
associations and feelings, even when these are contrary to one’s conscious or declared beliefs.
They are automatically activated and may occur unconsciously (Metzl et al., 2018, 2020; Van
Ryn et al. 2011).
Inclusive environments: Environmental and organizational cultures in which faculty, students,
staff, and administrators with diverse characteristics thrive. Inclusive environments require
intentionality and embrace differences, not merely tolerate them. Everyone works to ensure the
perspectives and experiences of others are invited, welcomed, acknowledged, and respected.
Inequities: Characterized by a lack of equity, injustice, unfairness.
Informatics: The intersection between the work of stakeholders across the health and
healthcare delivery system who seek to improve outcomes, lower costs, increase safety and
promote the use of high-quality services. It is frequently confused with data science, big data,
health information management and data analytics, informatics is the overarching field of study
that pulls all these subdomains into one discipline focused on improving health and healthcare.
Emerging topics like artificial intelligence and machine learning are incorporating in the field of
informatics (AMIA, 2021).
Information and Communications Technologies (ICT): Technologies that provide access to
information through telecommunications, including the internet, telephones, cell phones,
wireless signals, networks, satellite systems, telehealth/telenursing, and video conferencing.
Innovation: A great idea to develop and deliver new or improved health policies, systems,
products and technologies, and services and delivery methods that improve people’s health
(WHO Health Innovation Group, 2021).
Integration: An experience designed to provide the student with an opportunity to synthesize
the knowledge and skills acquired during previous and current coursework and learning
experiences.
Intentional change theory: The essential components and processes of desirable, sustainable
change in one’s behavior, thoughts, feelings, and perceptions. The “change” maybe in a person’s
actions, habits, competencies, or aspirations as well as in the way one feels in certain situations
or around certain people. The change may impact how one looks at events at work or in life.
The change is “desired” in that person wishes it so or would like to occur and is “sustainable” in
that it endures and lasts a relatively long time (Boyatzis, 2006).
Interdisciplinary: Refers to a group of healthcare providers with various areas of expertise who
work together toward the goals of their clients.
Interoperability: The ability of different information systems, devices, and applications
(systems) to access, exchange, integrate, and cooperatively use data in a coordinated manner,
within and across organizational, regional, and national boundaries to provide timely and
seamless portability of information and optimize the health of individuals and populations
globally. Health data exchange architectures, application interfaces, and standards enable data
to be accessed and shared appropriately and securely across the complete spectrum of care,
within all applicable settings and with relevant stakeholders, including the individual.
60 THE ESSENTIALS: CORE COMPETENCIES FOR PROFESSIONAL NURSING EDUCATION
Implicit and unconscious biases: The tendency to process information based on unconscious
associations and feelings, even when these are contrary to one’s conscious or declared beliefs.
They are automatically activated and may occur unconsciously (Metzl et al., 2018, 2020; Van
Ryn et al. 2011).
Inclusive environments: Environmental and organizational cultures in which faculty, students,
staff, and administrators with diverse characteristics thrive. Inclusive environments require
intentionality and embrace differences, not merely tolerate them. Everyone works to ensure the
perspectives and experiences of others are invited, welcomed, acknowledged, and respected.
Inequities: Characterized by a lack of equity, injustice, unfairness.
Informatics: The intersection between the work of stakeholders across the health and
healthcare delivery system who seek to improve outcomes, lower costs, increase safety and
promote the use of high-quality services. It is frequently confused with data science, big data,
health information management and data analytics, informatics is the overarching field of study
that pulls all these subdomains into one discipline focused on improving health and healthcare.
Emerging topics like artificial intelligence and machine learning are incorporating in the field of
informatics (AMIA, 2021).
Information and Communications Technologies (ICT): Technologies that provide access to
information through telecommunications, including the internet, telephones, cell phones,
wireless signals, networks, satellite systems, telehealth/telenursing, and video conferencing.
Innovation: A great idea to develop and deliver new or improved health policies, systems,
products and technologies, and services and delivery methods that improve people’s health
(WHO Health Innovation Group, 2021).
Integration: An experience designed to provide the student with an opportunity to synthesize
the knowledge and skills acquired during previous and current coursework and learning
experiences.
Intentional change theory: The essential components and processes of desirable, sustainable
change in one’s behavior, thoughts, feelings, and perceptions. The “change” maybe in a person’s
actions, habits, competencies, or aspirations as well as in the way one feels in certain situations
or around certain people. The change may impact how one looks at events at work or in life.
The change is “desired” in that person wishes it so or would like to occur and is “sustainable” in
that it endures and lasts a relatively long time (Boyatzis, 2006).
Interdisciplinary: Refers to a group of healthcare providers with various areas of expertise who
work together toward the goals of their clients.
Interoperability: The ability of different information systems, devices, and applications
(systems) to access, exchange, integrate, and cooperatively use data in a coordinated manner,
within and across organizational, regional, and national boundaries to provide timely and
seamless portability of information and optimize the health of individuals and populations
globally. Health data exchange architectures, application interfaces, and standards enable data
to be accessed and shared appropriately and securely across the complete spectrum of care,
within all applicable settings and with relevant stakeholders, including the individual.
60 THE ESSENTIALS: CORE COMPETENCIES FOR PROFESSIONAL NURSING EDUCATION