よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
参考資料6_THE ESSENTIALS: CORE COMPETENCIES FOR PROFESSIONAL NURSING EDUCATION (2021 American Association of Colleges of Nursing) (49 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mext.go.jp/b_menu/shingi/chousa/koutou/125/mext_00004.html |
| 出典情報 | 看護学教育モデル・コア・カリキュラムの改訂に関する連絡調整委員会(第1回 7/19)《文部科学省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
© 2021 American Association of Colleges of Nursing. All rights reserved.
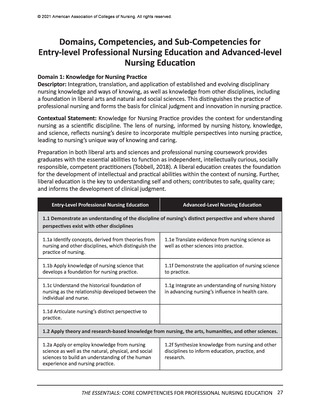
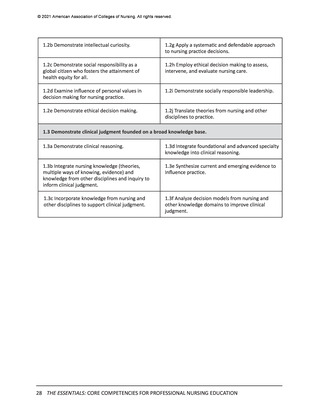
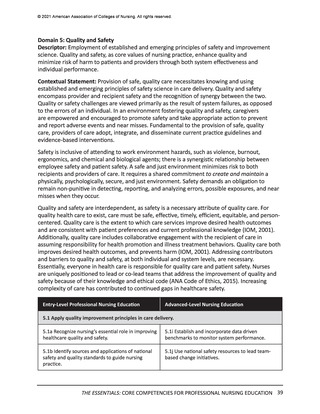
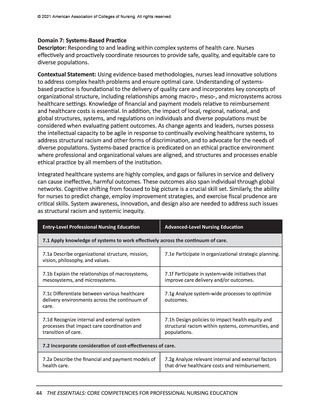
Domain 7: Systems-Based Practice
Descriptor: Responding to and leading within complex systems of health care. Nurses
effectively and proactively coordinate resources to provide safe, quality, and equitable care to
diverse populations.
Contextual Statement: Using evidence-based methodologies, nurses lead innovative solutions
to address complex health problems and ensure optimal care. Understanding of systemsbased practice is foundational to the delivery of quality care and incorporates key concepts of
organizational structure, including relationships among macro-, meso-, and microsystems across
healthcare settings. Knowledge of financial and payment models relative to reimbursement
and healthcare costs is essential. In addition, the impact of local, regional, national, and
global structures, systems, and regulations on individuals and diverse populations must be
considered when evaluating patient outcomes. As change agents and leaders, nurses possess
the intellectual capacity to be agile in response to continually evolving healthcare systems, to
address structural racism and other forms of discrimination, and to advocate for the needs of
diverse populations. Systems-based practice is predicated on an ethical practice environment
where professional and organizational values are aligned, and structures and processes enable
ethical practice by all members of the institution.
Integrated healthcare systems are highly complex, and gaps or failures in service and delivery
can cause ineffective, harmful outcomes. These outcomes also span individual through global
networks. Cognitive shifting from focused to big picture is a crucial skill set. Similarly, the ability
for nurses to predict change, employ improvement strategies, and exercise fiscal prudence are
critical skills. System awareness, innovation, and design also are needed to address such issues
as structural racism and systemic inequity.
Entry-Level Professional Nursing Education
Advanced-Level Nursing Education
7.1 Apply knowledge of systems to work effectively across the continuum of care.
7.1a Describe organizational structure, mission,
vision, philosophy, and values.
7.1e Participate in organizational strategic planning.
7.1b Explain the relationships of macrosystems,
mesosystems, and microsystems.
7.1f Participate in system-wide initiatives that
improve care delivery and/or outcomes.
7.1c Differentiate between various healthcare
delivery environments across the continuum of
care.
7.1g Analyze system-wide processes to optimize
outcomes.
7.1d Recognize internal and external system
processes that impact care coordination and
transition of care.
7.1h Design policies to impact health equity and
structural racism within systems, communities, and
populations.
7.2 Incorporate consideration of cost-effectiveness of care.
7.2a Describe the financial and payment models of
health care.
7.2g Analyze relevant internal and external factors
that drive healthcare costs and reimbursement.
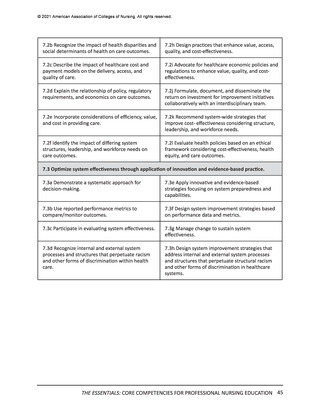
44 THE ESSENTIALS: CORE COMPETENCIES FOR PROFESSIONAL NURSING EDUCATION
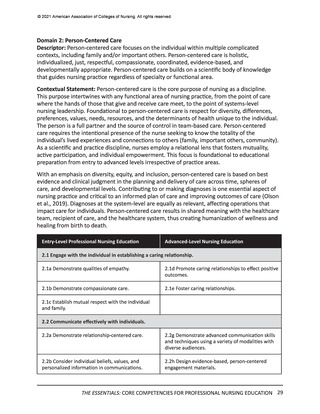
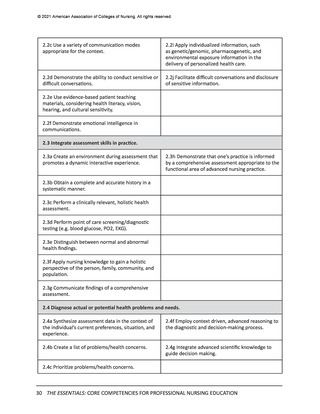
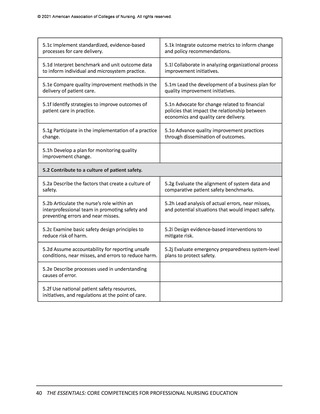
Domain 7: Systems-Based Practice
Descriptor: Responding to and leading within complex systems of health care. Nurses
effectively and proactively coordinate resources to provide safe, quality, and equitable care to
diverse populations.
Contextual Statement: Using evidence-based methodologies, nurses lead innovative solutions
to address complex health problems and ensure optimal care. Understanding of systemsbased practice is foundational to the delivery of quality care and incorporates key concepts of
organizational structure, including relationships among macro-, meso-, and microsystems across
healthcare settings. Knowledge of financial and payment models relative to reimbursement
and healthcare costs is essential. In addition, the impact of local, regional, national, and
global structures, systems, and regulations on individuals and diverse populations must be
considered when evaluating patient outcomes. As change agents and leaders, nurses possess
the intellectual capacity to be agile in response to continually evolving healthcare systems, to
address structural racism and other forms of discrimination, and to advocate for the needs of
diverse populations. Systems-based practice is predicated on an ethical practice environment
where professional and organizational values are aligned, and structures and processes enable
ethical practice by all members of the institution.
Integrated healthcare systems are highly complex, and gaps or failures in service and delivery
can cause ineffective, harmful outcomes. These outcomes also span individual through global
networks. Cognitive shifting from focused to big picture is a crucial skill set. Similarly, the ability
for nurses to predict change, employ improvement strategies, and exercise fiscal prudence are
critical skills. System awareness, innovation, and design also are needed to address such issues
as structural racism and systemic inequity.
Entry-Level Professional Nursing Education
Advanced-Level Nursing Education
7.1 Apply knowledge of systems to work effectively across the continuum of care.
7.1a Describe organizational structure, mission,
vision, philosophy, and values.
7.1e Participate in organizational strategic planning.
7.1b Explain the relationships of macrosystems,
mesosystems, and microsystems.
7.1f Participate in system-wide initiatives that
improve care delivery and/or outcomes.
7.1c Differentiate between various healthcare
delivery environments across the continuum of
care.
7.1g Analyze system-wide processes to optimize
outcomes.
7.1d Recognize internal and external system
processes that impact care coordination and
transition of care.
7.1h Design policies to impact health equity and
structural racism within systems, communities, and
populations.
7.2 Incorporate consideration of cost-effectiveness of care.
7.2a Describe the financial and payment models of
health care.
7.2g Analyze relevant internal and external factors
that drive healthcare costs and reimbursement.
44 THE ESSENTIALS: CORE COMPETENCIES FOR PROFESSIONAL NURSING EDUCATION