よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
参考資料6_THE ESSENTIALS: CORE COMPETENCIES FOR PROFESSIONAL NURSING EDUCATION (2021 American Association of Colleges of Nursing) (20 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mext.go.jp/b_menu/shingi/chousa/koutou/125/mext_00004.html |
| 出典情報 | 看護学教育モデル・コア・カリキュラムの改訂に関する連絡調整委員会(第1回 7/19)《文部科学省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
© 2021 American Association of Colleges of Nursing. All rights reserved.
Competencies and Sub-Competencies
The competencies identified in this Essentials document provide a bridge between the current
and future needs of practice and the requisite education to prepare a competent practitioner.
Competence develops over time, is progressive, and reflects the impact of internal and
external factors and experiences of the student. Internal factors include education, experience,
knowledge, and professional orientation, among others. External forces include the complexity
of the learning experience and professional autonomy. While knowledge is essential to the
development of competence, it does not in and of itself validate competence (Currier, 2019).
Rather, learners progress to successive levels of competence by demonstrating achievement of
expectations across the span of their education and practice experience. Students are successful
when they meet and sustain measurable competence at each level of performance expectation
and are able to transfer their competence across different practice experiences and settings
(Josiah Macy Foundation, 2017).
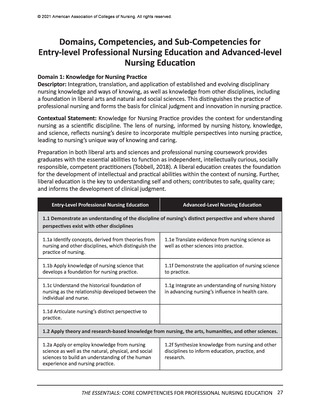
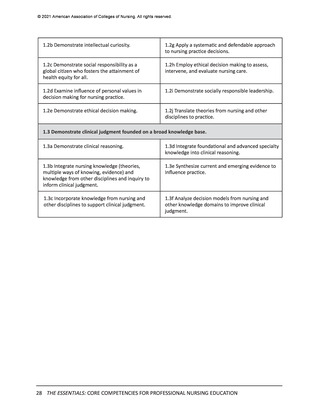
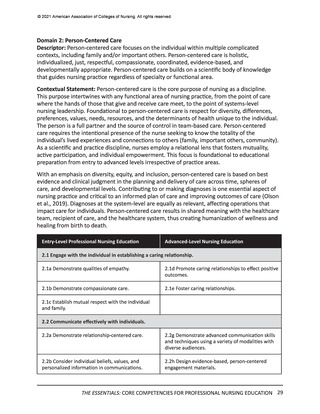
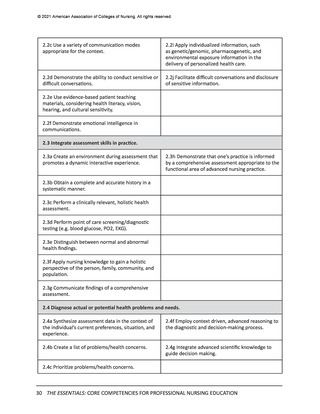
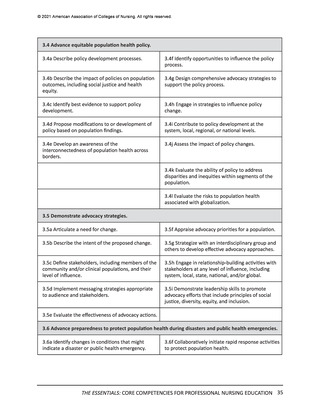
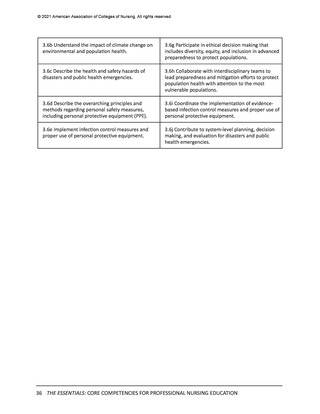
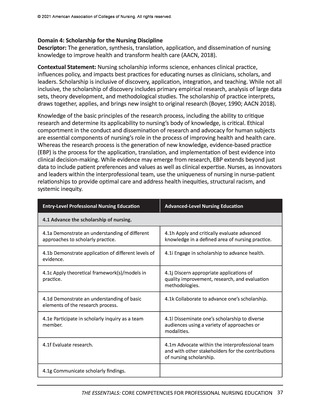
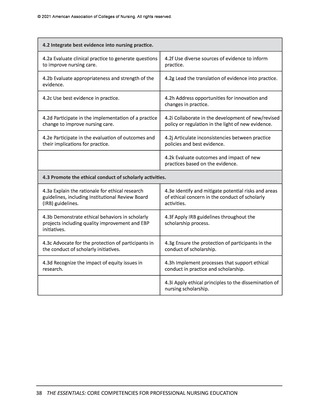
All competencies, organized within the 10 domains, are broad in scope and cross all levels
and areas of nursing practice. The competency is intentionally written as a short statement;
therefore, it is necessary to be familiar with the contextual statement within the parent
domain to fully understand the competency. In other words, the competency is interpreted
as a component within the domain. It also should be noted that there is intentional overlap
of competencies in several domains to account for differences in the competency or subcompetency context in different domains.
Each competency statement has multiple sub-competencies written at two levels to reflect
learner expectations for entry-level and advanced nursing education. These sub-competencies
are designed to ‘paint a picture’ of how the competency is achieved at each level. The subcompetencies are designed to be understandable, observable, and measurable by learner,
faculty, and future employers. Competencies mature over time and become more sophisticated
with ongoing practice.
THE ESSENTIALS: CORE COMPETENCIES FOR PROFESSIONAL NURSING EDUCATION 15
Competencies and Sub-Competencies
The competencies identified in this Essentials document provide a bridge between the current
and future needs of practice and the requisite education to prepare a competent practitioner.
Competence develops over time, is progressive, and reflects the impact of internal and
external factors and experiences of the student. Internal factors include education, experience,
knowledge, and professional orientation, among others. External forces include the complexity
of the learning experience and professional autonomy. While knowledge is essential to the
development of competence, it does not in and of itself validate competence (Currier, 2019).
Rather, learners progress to successive levels of competence by demonstrating achievement of
expectations across the span of their education and practice experience. Students are successful
when they meet and sustain measurable competence at each level of performance expectation
and are able to transfer their competence across different practice experiences and settings
(Josiah Macy Foundation, 2017).
All competencies, organized within the 10 domains, are broad in scope and cross all levels
and areas of nursing practice. The competency is intentionally written as a short statement;
therefore, it is necessary to be familiar with the contextual statement within the parent
domain to fully understand the competency. In other words, the competency is interpreted
as a component within the domain. It also should be noted that there is intentional overlap
of competencies in several domains to account for differences in the competency or subcompetency context in different domains.
Each competency statement has multiple sub-competencies written at two levels to reflect
learner expectations for entry-level and advanced nursing education. These sub-competencies
are designed to ‘paint a picture’ of how the competency is achieved at each level. The subcompetencies are designed to be understandable, observable, and measurable by learner,
faculty, and future employers. Competencies mature over time and become more sophisticated
with ongoing practice.
THE ESSENTIALS: CORE COMPETENCIES FOR PROFESSIONAL NURSING EDUCATION 15