よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
参考資料6_THE ESSENTIALS: CORE COMPETENCIES FOR PROFESSIONAL NURSING EDUCATION (2021 American Association of Colleges of Nursing) (64 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mext.go.jp/b_menu/shingi/chousa/koutou/125/mext_00004.html |
| 出典情報 | 看護学教育モデル・コア・カリキュラムの改訂に関する連絡調整委員会(第1回 7/19)《文部科学省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
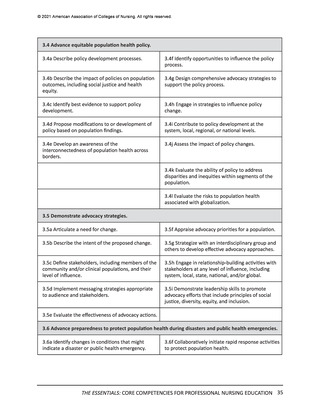
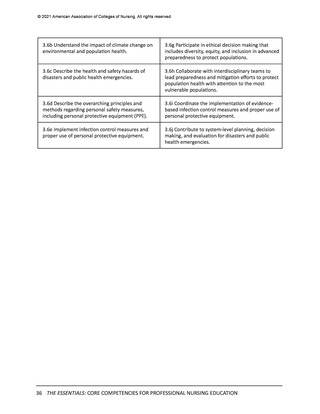
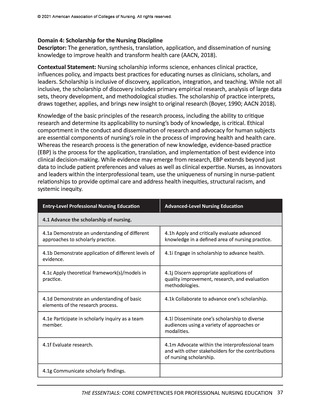
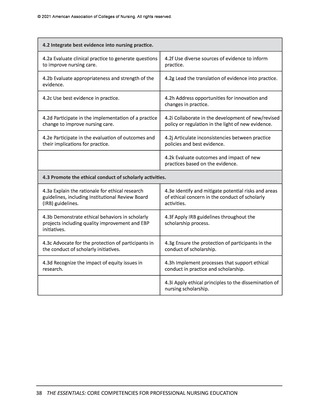
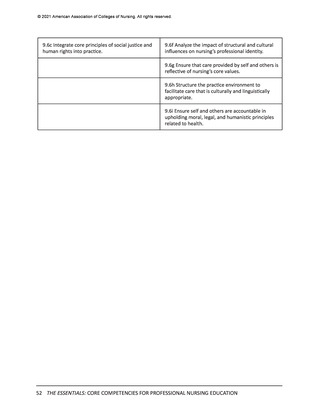
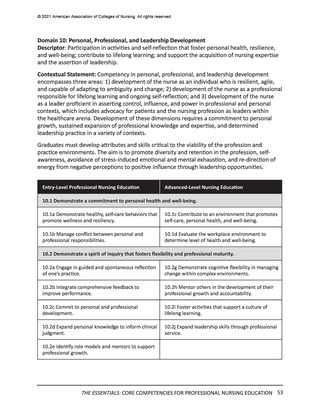
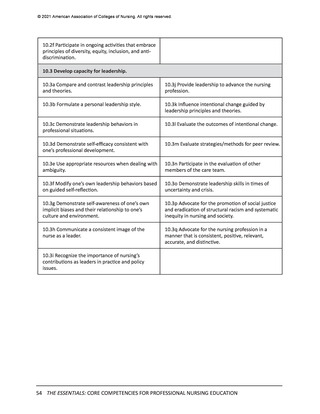
© 2021 American Association of Colleges of Nursing. All rights reserved.
Family: An individual’s closest support structure that is inclusive of birth family, single parent
families, blended families, families with stepparents, and families with homosexual parents to
name a few. The concept of the contemporary family has evolved into a fluid ideology that is
constantly shifting and changing throughout society.
Health disparities: “A particular type of health difference that is closely linked with economic,
social, or environmental disadvantage. Health disparities adversely affect groups of people who
have systematically experienced greater social or economic obstacles to health based on their
racial or ethnic group, religion, socioeconomic status, gender, age, or mental health; cognitive,
sensory, or physical disability; sexual orientation or gender identity; geographic location; or
other characteristics historically linked to discrimination or exclusion” (US Department of Health
and Human Services (2010).
Health equity: When every person has an opportunity to attain his or her full health potential”
and no one is “disadvantaged from achieving this potential because of social position or other
socially determined circumstances (National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine,
2017). Health inequities are reflected in differences in length of life; quality of life; rates of
disease, disability, and death; severity of disease; and access to treatment.
Health inequity: The distribution and allocation of power and resources differentially, which
manifest in unequal social, economic, and environmental conditions (National Academies of
Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, 2017).
Health Information Technology (HIT): The electronic systems healthcare professionals and
patients use to store, share, and analyze health information. HIT consists of many types of
applications such as Electronic Health Records, personal health records, electronic prescribing,
mobile applications, social networks, monitors, wearables, nanotechnology, genomics, and
robotics (Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology [ONC], 2018).
Healthcare team: The collective of individuals who contribute to the care and treatment of an
individual, family, group, or population.
Healthy lifestyle: A way of living that lowers the risk of being seriously ill or dying early.
Scientific studies have identified certain types of behavior that contribute to the development
of noncommunicable diseases and early death. Health is not only just about avoiding disease. It
involves physical, mental and social wellbeing.
Holistic admissions review: An admissions strategy that assesses an applicant’s unique
experiences alongside traditional measures of academic achievement, such as grades and test
scores. This process is used to help schools consider a broad range of factors reflecting the
applicant’s academic readiness, contribution to the incoming class, and potential for success
both in school and later as a professional.
Holistic nursing: “All nursing practice that has healing the whole person as its goal” (American
Holistic Nurses’ Association, 1998).
THE ESSENTIALS: CORE COMPETENCIES FOR PROFESSIONAL NURSING EDUCATION 59
Family: An individual’s closest support structure that is inclusive of birth family, single parent
families, blended families, families with stepparents, and families with homosexual parents to
name a few. The concept of the contemporary family has evolved into a fluid ideology that is
constantly shifting and changing throughout society.
Health disparities: “A particular type of health difference that is closely linked with economic,
social, or environmental disadvantage. Health disparities adversely affect groups of people who
have systematically experienced greater social or economic obstacles to health based on their
racial or ethnic group, religion, socioeconomic status, gender, age, or mental health; cognitive,
sensory, or physical disability; sexual orientation or gender identity; geographic location; or
other characteristics historically linked to discrimination or exclusion” (US Department of Health
and Human Services (2010).
Health equity: When every person has an opportunity to attain his or her full health potential”
and no one is “disadvantaged from achieving this potential because of social position or other
socially determined circumstances (National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine,
2017). Health inequities are reflected in differences in length of life; quality of life; rates of
disease, disability, and death; severity of disease; and access to treatment.
Health inequity: The distribution and allocation of power and resources differentially, which
manifest in unequal social, economic, and environmental conditions (National Academies of
Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, 2017).
Health Information Technology (HIT): The electronic systems healthcare professionals and
patients use to store, share, and analyze health information. HIT consists of many types of
applications such as Electronic Health Records, personal health records, electronic prescribing,
mobile applications, social networks, monitors, wearables, nanotechnology, genomics, and
robotics (Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology [ONC], 2018).
Healthcare team: The collective of individuals who contribute to the care and treatment of an
individual, family, group, or population.
Healthy lifestyle: A way of living that lowers the risk of being seriously ill or dying early.
Scientific studies have identified certain types of behavior that contribute to the development
of noncommunicable diseases and early death. Health is not only just about avoiding disease. It
involves physical, mental and social wellbeing.
Holistic admissions review: An admissions strategy that assesses an applicant’s unique
experiences alongside traditional measures of academic achievement, such as grades and test
scores. This process is used to help schools consider a broad range of factors reflecting the
applicant’s academic readiness, contribution to the incoming class, and potential for success
both in school and later as a professional.
Holistic nursing: “All nursing practice that has healing the whole person as its goal” (American
Holistic Nurses’ Association, 1998).
THE ESSENTIALS: CORE COMPETENCIES FOR PROFESSIONAL NURSING EDUCATION 59