よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
参考資料6_THE ESSENTIALS: CORE COMPETENCIES FOR PROFESSIONAL NURSING EDUCATION (2021 American Association of Colleges of Nursing) (23 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mext.go.jp/b_menu/shingi/chousa/koutou/125/mext_00004.html |
| 出典情報 | 看護学教育モデル・コア・カリキュラムの改訂に関する連絡調整委員会(第1回 7/19)《文部科学省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
© 2021 American Association of Colleges of Nursing. All rights reserved.
Implementing the Essentials: Considerations for Curriculum
The domains, competencies, and concepts presented in the Essentials provide the platform for
curriculum design and program assessment with an intent to produce consistency in outcomes
expected of graduates. Although these are major elements incorporated within a curriculum
for learning and assessment, they are not to be interpreted as representing the curriculum
in its entirety. In other words, it is not intended for courses within nursing curricula to mirror
the 10 domains and eight concepts. Instead, the elements used as the Essentials framework
(domains, concepts, and competencies) should be integrated throughout and across the
curriculum. A scaffolded approach ensures students interface with competencies in multiple
contexts and with increasing complexity. Nursing programs have a great deal of flexibility in
the development and design of curricula, thus preserving the ability of nursing programs to be
unique or innovative.
Outcomes, when referred to as student learning outcomes, describe the desired outcomes
of the graduate at the completion of the program. The student learning outcomes will reflect
attainment of all competencies in addition to any relevant specialty/role competencies and
other identified expectations. Course design within curricula reflect the expectations of student
learning with clear linkage from course objectives/competencies from within and across courses
to end of program student learning outcomes, written as course learning outcomes or course
competencies. For this reason, course outcomes should link to the Essentials competencies
and concepts. Intentional teaching strategies are designed and incorporated throughout the
curriculum in multiple contexts and with increasing complexity to provide students multiple
opportunities for learning and demonstrating competencies. For the foreseeable future,
minimum requirements for practicum experiences are deemed important to provide consistent
and quality preparation at both the entry- and advanced-levels for professional nursing practice.
Competencies are assessed as the learner progresses throughout the program; therefore, a
robust program assessment plan is needed to measure students’ achievement of competencies
by the end of the program. Some programs may wish to create “progression indicators” at
specified points within a program of study to track learners’ achievement of competencies.
To demonstrate the integration of competencies across multiple domains with increasing
complexity, performance assessments should be integrated in the curriculum throughout the
program of study. As such, assessments are performance based and serve as both a learning
experience and an evaluation tool. Performance assessment is a multidimensional process,
integral to learning, that involves observation and judgment of each student’s performance
on the basis of explicit criteria, with feedback to the student for improving learning
and competency.
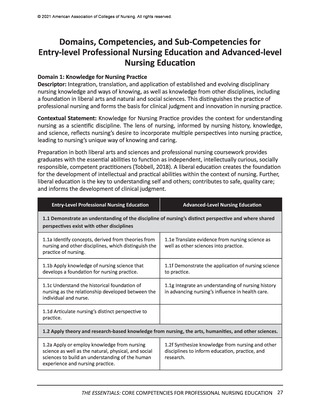
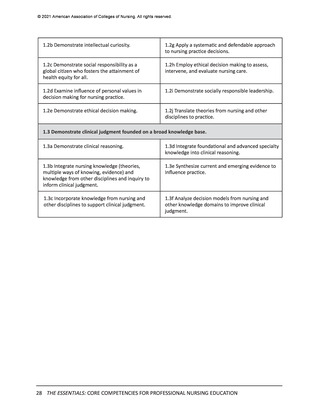
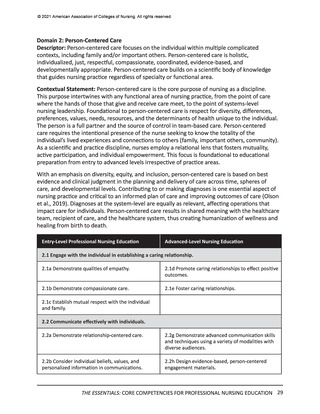
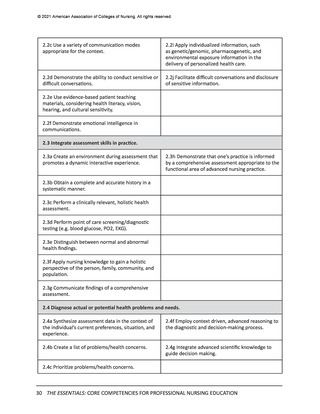
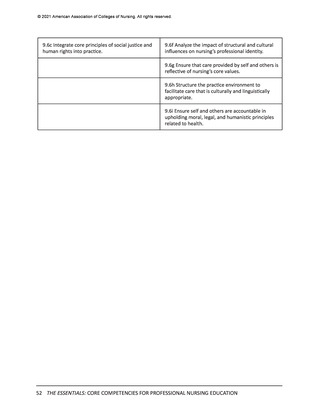
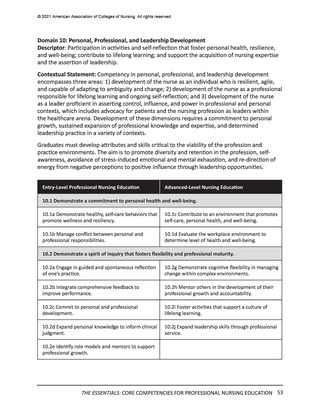
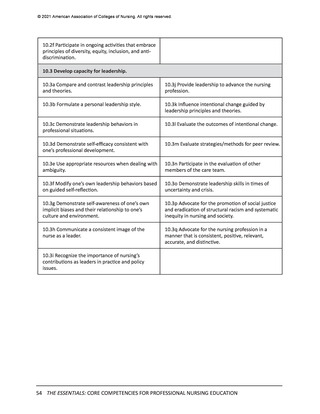
In the previous section, the Essentials Model featuring two levels of professional nursing
education (entry and advanced) was introduced. While the domains, competencies, and
concepts are identical for both entry and advanced levels of education, sub-competencies are
used to differentiate expectations for entry (Level 1) and advanced (Level 2) professional nursing
education (see Figure 1). These two levels of sub-competencies reflect the educational stages
of nurses—as they enter professional nursing practice and as they advance their education—
regardless of the program of study they are completing to advance their education. The
following sections detail the expectations for curricula at each of these two levels.
18 THE ESSENTIALS: CORE COMPETENCIES FOR PROFESSIONAL NURSING EDUCATION
Implementing the Essentials: Considerations for Curriculum
The domains, competencies, and concepts presented in the Essentials provide the platform for
curriculum design and program assessment with an intent to produce consistency in outcomes
expected of graduates. Although these are major elements incorporated within a curriculum
for learning and assessment, they are not to be interpreted as representing the curriculum
in its entirety. In other words, it is not intended for courses within nursing curricula to mirror
the 10 domains and eight concepts. Instead, the elements used as the Essentials framework
(domains, concepts, and competencies) should be integrated throughout and across the
curriculum. A scaffolded approach ensures students interface with competencies in multiple
contexts and with increasing complexity. Nursing programs have a great deal of flexibility in
the development and design of curricula, thus preserving the ability of nursing programs to be
unique or innovative.
Outcomes, when referred to as student learning outcomes, describe the desired outcomes
of the graduate at the completion of the program. The student learning outcomes will reflect
attainment of all competencies in addition to any relevant specialty/role competencies and
other identified expectations. Course design within curricula reflect the expectations of student
learning with clear linkage from course objectives/competencies from within and across courses
to end of program student learning outcomes, written as course learning outcomes or course
competencies. For this reason, course outcomes should link to the Essentials competencies
and concepts. Intentional teaching strategies are designed and incorporated throughout the
curriculum in multiple contexts and with increasing complexity to provide students multiple
opportunities for learning and demonstrating competencies. For the foreseeable future,
minimum requirements for practicum experiences are deemed important to provide consistent
and quality preparation at both the entry- and advanced-levels for professional nursing practice.
Competencies are assessed as the learner progresses throughout the program; therefore, a
robust program assessment plan is needed to measure students’ achievement of competencies
by the end of the program. Some programs may wish to create “progression indicators” at
specified points within a program of study to track learners’ achievement of competencies.
To demonstrate the integration of competencies across multiple domains with increasing
complexity, performance assessments should be integrated in the curriculum throughout the
program of study. As such, assessments are performance based and serve as both a learning
experience and an evaluation tool. Performance assessment is a multidimensional process,
integral to learning, that involves observation and judgment of each student’s performance
on the basis of explicit criteria, with feedback to the student for improving learning
and competency.
In the previous section, the Essentials Model featuring two levels of professional nursing
education (entry and advanced) was introduced. While the domains, competencies, and
concepts are identical for both entry and advanced levels of education, sub-competencies are
used to differentiate expectations for entry (Level 1) and advanced (Level 2) professional nursing
education (see Figure 1). These two levels of sub-competencies reflect the educational stages
of nurses—as they enter professional nursing practice and as they advance their education—
regardless of the program of study they are completing to advance their education. The
following sections detail the expectations for curricula at each of these two levels.
18 THE ESSENTIALS: CORE COMPETENCIES FOR PROFESSIONAL NURSING EDUCATION