よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
資料1-2 カルベジロール 調査結果報告書及び添付文書[1.9MB] (24 ページ)
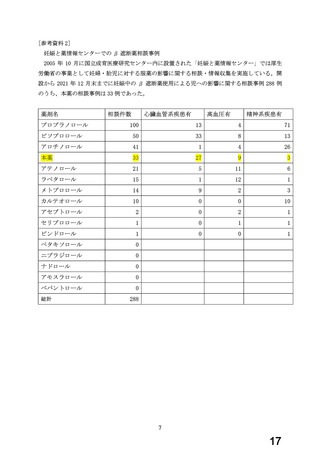
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_38855.html |
| 出典情報 | 薬事・食品衛生審議会 薬事分科会医薬品等安全対策部会安全対策調査会(令和5年度第15回 3/26)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
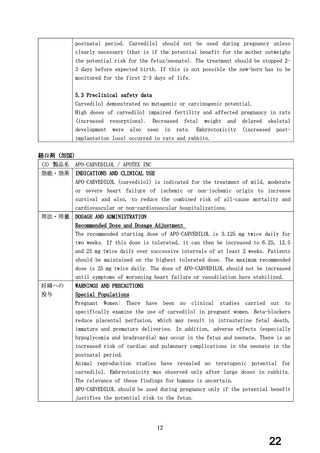
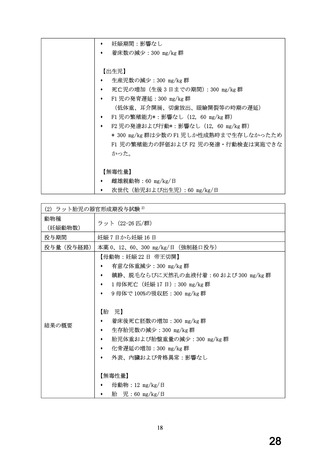
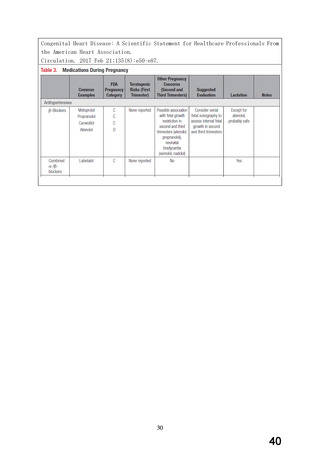
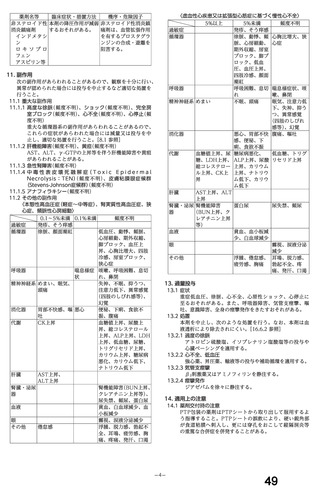
経口剤(豪州)
(4) 製品名 Dilatrend / Pharmaco Australia Ltd
効能・効果
4.1 Therapeutic Indications
Dilatrend is indicated for the treatment of hypertension. Data have not been
provided to support the use of this drug in renovascular disease.
Dilatrend is indicated for the treatment of patients with symptomatic mild to
severe (NYHA Class II - IV) congestive heart failure (CHF) as an adjunct to
conventional
treatments
(e.g.
diuretics,
digoxin,
ACE
inhibitors
and
vasodilators).
用法・用量
4.2 DOSE AND METHOD OF ADMINISTRATION
Hypertension
Once daily dosing is recommended.
Adults. The recommended dose for initiation of therapy is 12.5 mg once a day
for the first two days. Thereafter the recommended dosage is 25 mg once a
day. If necessary, the dosage may subsequently be increased at intervals of
at least two weeks up to the recommended maximum daily dose of 50 mg given
once or twice daily.
Symptomatic Congestive Heart Failure:
Dosage must be individualised and closely monitored by a physician during uptitration.
The recommended starting dose is 3.125 mg twice daily for 2 weeks. If this
dose is tolerated, the dosage may subsequently be increased, at intervals of
not less than two weeks, to 6.25 mg twice daily, followed by 12.5 mg twice
daily, then 25 mg twice daily. Dosing should be increased to the highest level
tolerated by the patient.
The recommended maximum daily dose is 25 mg twice daily in patients with mild
or moderate CHF weighing less than 85 kg. In patients with mild or moderate
CHF weighing more than 85 kg, the recommended maximum daily dose is 50 mg
twice daily. For all patients with severe CHF the recommended maximum daily
dose is 25 mg twice daily.
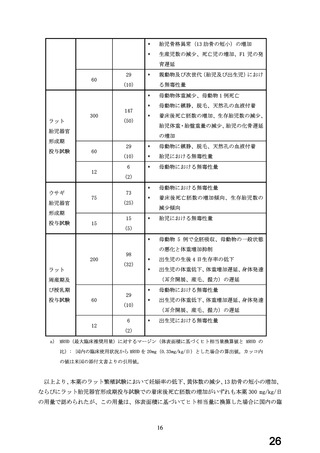
妊婦への
4.6 Fertility, Pregnancy and Lactation
投与
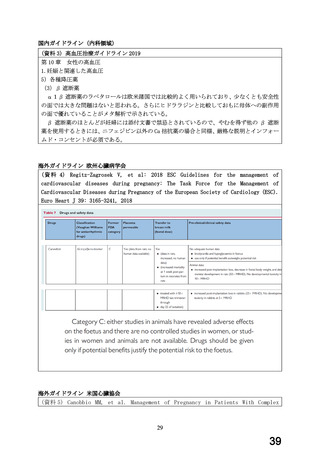
Use in pregnancy(Category C)
There is no adequate clinical experience with carvedilol in pregnant women.
Studies in rats have shown that carvedilol and/or its metabolites cross the
placental barrier. Beta-blockers may cause bradycardia in the foetus and
newborn infant. During the later stages of pregnancy and parturition, these
drugs should therefore only be given after weighing the needs of the mother
against the risk to the foetus.
Studies in rats and rabbits showed carvedilol was not teratogenic at doses up
to 300 and 75 mg/kg/day, respectively. Carvedilol was embryotoxic and
foetotoxic at doses greater than 60 mg/kg/day in rats and 15 mg/kg/day in
rabbits. Maternal toxicity was noted in rats and rabbits at doses greater than
13
23
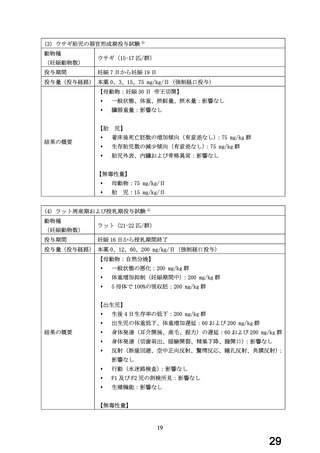
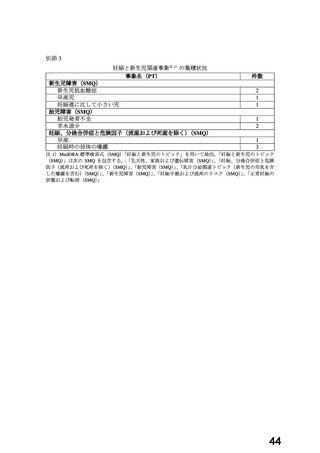
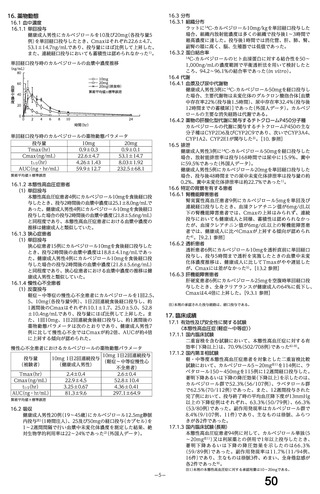
(4) 製品名 Dilatrend / Pharmaco Australia Ltd
効能・効果
4.1 Therapeutic Indications
Dilatrend is indicated for the treatment of hypertension. Data have not been
provided to support the use of this drug in renovascular disease.
Dilatrend is indicated for the treatment of patients with symptomatic mild to
severe (NYHA Class II - IV) congestive heart failure (CHF) as an adjunct to
conventional
treatments
(e.g.
diuretics,
digoxin,
ACE
inhibitors
and
vasodilators).
用法・用量
4.2 DOSE AND METHOD OF ADMINISTRATION
Hypertension
Once daily dosing is recommended.
Adults. The recommended dose for initiation of therapy is 12.5 mg once a day
for the first two days. Thereafter the recommended dosage is 25 mg once a
day. If necessary, the dosage may subsequently be increased at intervals of
at least two weeks up to the recommended maximum daily dose of 50 mg given
once or twice daily.
Symptomatic Congestive Heart Failure:
Dosage must be individualised and closely monitored by a physician during uptitration.
The recommended starting dose is 3.125 mg twice daily for 2 weeks. If this
dose is tolerated, the dosage may subsequently be increased, at intervals of
not less than two weeks, to 6.25 mg twice daily, followed by 12.5 mg twice
daily, then 25 mg twice daily. Dosing should be increased to the highest level
tolerated by the patient.
The recommended maximum daily dose is 25 mg twice daily in patients with mild
or moderate CHF weighing less than 85 kg. In patients with mild or moderate
CHF weighing more than 85 kg, the recommended maximum daily dose is 50 mg
twice daily. For all patients with severe CHF the recommended maximum daily
dose is 25 mg twice daily.
妊婦への
4.6 Fertility, Pregnancy and Lactation
投与
Use in pregnancy(Category C)
There is no adequate clinical experience with carvedilol in pregnant women.
Studies in rats have shown that carvedilol and/or its metabolites cross the
placental barrier. Beta-blockers may cause bradycardia in the foetus and
newborn infant. During the later stages of pregnancy and parturition, these
drugs should therefore only be given after weighing the needs of the mother
against the risk to the foetus.
Studies in rats and rabbits showed carvedilol was not teratogenic at doses up
to 300 and 75 mg/kg/day, respectively. Carvedilol was embryotoxic and
foetotoxic at doses greater than 60 mg/kg/day in rats and 15 mg/kg/day in
rabbits. Maternal toxicity was noted in rats and rabbits at doses greater than
13
23